Contpark specializes in offering a robust terminal management solution. Its platform includes features for real-time visibility, workflow automation, and security, simplifying terminal operations and increasing productivity.
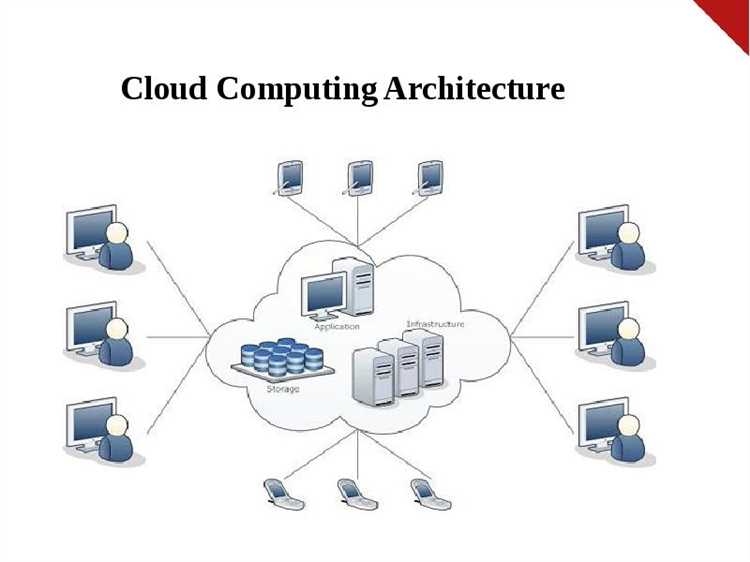
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing them with a flexible and scalable infrastructure to store and process their data. One of the key aspects of cloud computing is its seamless integration with cloud-based computing, a model that enables businesses to leverage the power of the cloud for various purposes.
Authorization and authentication are crucial components of cloud-based computing, ensuring that only approved individuals have access to sensitive data and resources. This is particularly important in manufacturing industries, where intellectual property and confidential information must be protected.
The continuous deployment of applications and software updates is made more efficient with cloud-based computing, as it allows for easy and fast distribution across multiple platforms. Document management and content management systems (CMS) also benefit from the scalability and flexibility provided by the cloud.
Load balancing and advertising are other key functions that can be enhanced through cloud integration. Load balancing ensures that resources are evenly distributed across servers, optimizing performance and improving user experience. Advertising campaigns can benefit from cloud-based analytics and monitoring, allowing businesses to track and optimize their marketing efforts.
Cloud security is a critical consideration in the integration of cloud computing and cloud-based computing. Multi-cloud and multi-tenancy models enable businesses to spread their data and applications across multiple cloud providers, ensuring redundancy and minimizing the risk of downtime. Cloud security measures such as encryption and access controls further protect sensitive data.
In the finance sector, cloud-based computing enables mobile banking and secure data migration. Data visualization and supply chain management (SCM) also benefit from cloud integration, allowing for real-time tracking and analysis of inventory and logistics.
Data transformation and orchestration are made easier with cloud-based computing, as it provides a scalable and flexible platform for processing large volumes of data. The API economy is also driving the integration of cloud computing, allowing businesses to leverage the capabilities of cloud-based services through standardized interfaces.
Small startups and large enterprises alike are benefiting from the integration of cloud computing and cloud-based computing. With the use of big data analytics, edge analytics, and predictive analytics, businesses can gain valuable insights from their data and make informed decisions.
Public cloud providers offer data backup and disaster recovery services, ensuring the availability and integrity of business-critical assets. Service level agreements (SLA) guarantee uptime and performance standards, giving businesses peace of mind.
Cloud integration is also transforming the field of online marketing, automating tasks such as campaign management and customer segmentation. The management and automation of business processes can be streamlined with the use of cloud-based tools and applications.
In conclusion, the integration of cloud computing and cloud-based computing offers a wide range of benefits to businesses across various industries. From authorization and manufacturing to project management and finance, cloud integration empowers businesses with scalable and flexible solutions for their data and computing needs.
In today’s digital landscape, cloud computing plays a significant role in the way businesses operate and deliver services to their customers. Cloud computing refers to the use of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data, instead of using a local server or personal computer. This approach offers several advantages, including scalability, availability, and cost-efficiency.
One of the key concepts in cloud computing is the integration of cloud-based computing. This involves combining different types of cloud environments, such as public, private, and hybrid clouds, to optimize resource allocation and meet specific business needs. Hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud infrastructure, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both while maintaining control over sensitive data.
The integration of cloud-based computing relies on a robust network infrastructure to facilitate seamless communication between different cloud environments and ensure continuous availability of services. This includes load balancing, which distributes network traffic across multiple servers to optimize performance and prevent overloading. On-demand provisioning and elastic scaling enable businesses to access and allocate resources dynamically, based on their current needs.
Data governance and security are critical aspects of cloud-based computing integration. Organizations must implement appropriate measures, such as encryption and firewall protection, to safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, vulnerability scanning and continuous deployment processes help identify and address potential security vulnerabilities in the cloud environment.
Furthermore, cloud integration enables the adoption of mobile and internet-based services. Mobile computing and platform-as-a-service (PaaS) solutions allow businesses to develop and deploy applications that can be accessed from any device, enhancing flexibility and productivity. Cloud-based architecture also facilitates data science and analytics, providing companies with valuable insights and enabling data-driven decision-making.
When integrated effectively, cloud-based computing offers numerous benefits across various industries, from finance and sales to advertising and finance. It empowers organizations to achieve scalability, agility, and cost-efficiency in their operations. Additionally, it enables reliable disaster recovery mechanisms and reduces the need for extensive physical infrastructure.
In conclusion, understanding cloud computing and the integration of cloud-based computing is essential for organizations seeking to leverage the advantages of the cloud. This involves adopting hybrid cloud models, implementing robust network infrastructure, ensuring data governance and security, and harnessing mobile computing and data analytics capabilities. By embracing the cloud, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance their performance, and drive innovation in the digital era.

Cloud-based computing is a growing trend in the field of IT, offering numerous advantages such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It encompasses various services and applications that are hosted on remote servers and accessed over the internet. These services include data processing, big data analytics, data protection, encryption, monitoring, and authorization.
Integration of cloud-based computing into an organization’s infrastructure can bring significant benefits. For instance, cloud-based servers offer elastic scaling, allowing businesses to quickly adjust their computing resources according to their needs. This flexibility ensures optimal performance and guarantees high availability to users.
Continuous integration and computing management can be achieved through the use of microservices architecture. This modular approach allows the development and deployment of independent services, which can be easily scaled and updated. Cloud-based computing also enables remote access to services, making collaboration and data sharing seamless. This is especially beneficial in fields such as education, sales, and enterprise resource planning (ERP).
Data backup, vulnerability scanning, and encryption ensure data protection and security in cloud-based computing environments. Additionally, cloud-based computing integration can provide a platform for social media analytics and digital transformation, enabling organizations to harness the power of social media data for business insights.
Moreover, cloud-based computing offers load balancing capabilities, which distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers. This ensures optimal resource utilization and performance, particularly in high-demand scenarios. Large-scale government projects can greatly benefit from the scalability and availability offered by cloud-based computing.
In conclusion, exploring and integrating cloud-based computing into an organization’s infrastructure can bring numerous advantages, such as scalability, flexibility, and enhanced performance. With its wide range of services and applications, cloud-based computing is transforming industries and enabling digital transformation.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing provides numerous benefits, especially for e-commerce businesses. By leveraging private cloud infrastructure, companies can ensure the security and privacy of their data, creating a more trustworthy environment for online transactions. This integration also enables scalability, allowing e-commerce platforms to handle high volumes of traffic during peak periods and enhance customer experiences.
For startups, the integration of cloud computing and cloud-based computing offers a cost-effective solution for disaster recovery. By storing data and applications in the cloud, startups can quickly recover in case of an unexpected event, reducing downtime and minimizing financial losses. This integration also provides startups with the flexibility to scale their operations without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing enables seamless orchestration of IoT devices. By leveraging the power of the cloud, businesses can efficiently collect, analyze, and act upon the massive volumes of data generated by IoT devices. This integration allows for automation and real-time decision-making, enhancing operational efficiency and enabling businesses to take advantage of the opportunities presented by the IoT.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing improves identity and access management (IAM) capabilities, enhancing data governance and security. By centralizing user authentication and authorization through the cloud, businesses can ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information. This integration also enables businesses to implement robust data governance policies, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and protecting against data breaches.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing offers network-as-a-service capabilities, improving overall efficiency. Businesses can leverage cloud-based networking solutions to optimize their network performance, reduce latency, and enhance user experiences. This integration also allows businesses to manage their network resources more effectively, allocating bandwidth and routing traffic dynamically based on demand.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing provides businesses with easy access to software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications and version control. By utilizing cloud-based services, businesses can access a wide range of applications without the need for installation and maintenance. This integration also ensures that businesses are always using the latest version of the software, eliminating compatibility issues and improving productivity.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing offers reliable data backup and analytics capabilities. By storing data in the cloud, businesses can efficiently back up their information and ensure data resilience in case of hardware failures or disasters. The integration of cloud-based computing also enables businesses to leverage advanced analytics tools and technologies, extracting valuable insights from their data to make informed decisions and drive business growth.
The integration of cloud computing and cloud-based computing has significant benefits for the healthcare industry. By leveraging cloud infrastructure, healthcare organizations can securely store and access patient data, enabling seamless collaboration and enhancing patient care. This integration also facilitates remote patient monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health conditions in real-time and provide timely interventions.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing strengthens firewall capabilities and improves overall reliability. By leveraging cloud-based firewalls, businesses can safeguard their cloud infrastructure and protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats. This integration also ensures high availability and reliability of services, as cloud providers often offer robust infrastructure and redundant systems to minimize downtime.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing offers data visualization capabilities, which are particularly beneficial for non-profit organizations. By visualizing data trends and patterns, non-profits can gain valuable insights into their operations and impact, making data-driven decisions to achieve their mission more effectively. This integration also enables non-profit organizations to leverage cloud-based collaboration tools, enhancing communication and collaboration with stakeholders.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing ensures compliance with service level agreements (SLAs) and industry regulations. Cloud providers typically offer SLAs that guarantee certain levels of performance and uptime. This integration allows businesses to meet their contractual obligations and ensures that their cloud services comply with industry-specific regulations, such as HIPAA for the healthcare industry or GDPR for organizations handling personal data.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing enables edge analytics capabilities, optimizing workload distribution. By processing data at the edge of the network, businesses can reduce latency and enhance real-time decision-making. This integration also allows for workload optimization, as businesses can dynamically allocate computing resources between the cloud and edge devices based on the requirements of their applications.
Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing provides businesses with data lake capabilities and virtual machine management. By leveraging cloud-based data lakes, businesses can store and analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, enabling advanced analytics and machine learning. This integration also simplifies virtual machine management, allowing businesses to quickly provision, scale, and optimize virtual machines based on their computational needs.

Integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing enhances data protection and content management capabilities. Cloud-based data protection solutions provide businesses with automated backup and disaster recovery processes, ensuring the integrity and availability of their data. This integration also enables businesses to utilize cloud-based content management systems (CMS), simplifying content creation, collaboration, and distribution across multiple channels.
Integration of cloud computing and cloud-based computing brings several challenges that organizations need to overcome in order to fully leverage the benefits of these technologies. One of the main challenges is resource pooling, where organizations need to efficiently allocate and manage computing resources across multiple cloud platforms. This requires a deep understanding of the different cloud platforms and their capabilities.
In addition, organizations need to take into consideration firewall and managed services when integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing. Firewalls are used to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, while managed services provide support and maintenance for the cloud infrastructure.
A key aspect of cloud-based computing integration is the selection of the right platform. Different platforms offer different capabilities and functionalities, and organizations need to choose the one that best aligns with their needs and objectives. Hybrid integration is also a challenge, as organizations need to seamlessly integrate their existing on-premise infrastructure with the cloud-based computing environment.
Furthermore, organizations need to consider the specific requirements of their industry when integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing. For example, e-commerce companies may need to focus on data management and monitoring for efficient online transactions, whereas manufacturing companies may require storage-as-a-service for large amounts of data.
Another challenge is ensuring the reliability and availability of the integrated cloud computing and cloud-based computing environment. Organizations need to implement robust data storage, backup, and continuous delivery mechanisms to avoid any disruptions to their operations.
Organizations also need to consider the vulnerability scanning and data sovereignty requirements when integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing. Vulnerability scanning helps identify any potential security vulnerabilities, while data sovereignty ensures that data is stored and processed in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Finally, integration of cloud computing and cloud-based computing requires organizations to adopt an agile and microservices approach. This allows for easier deployment, efficient container orchestration, and improved edge computing capabilities.
In summary, integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing brings both technical and strategic challenges that organizations need to address. By carefully considering factors such as platform selection, industry-specific requirements, reliability and availability, and security and compliance, organizations can successfully integrate these technologies and unlock their full potential.
Cloud computing and cloud-based computing bring numerous benefits to organizations, including increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, integrating these technologies requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some best practices to follow when integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing:
Multi-tenancy allows multiple users to share a single instance of a software application, reducing costs and improving resource utilization. When integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing, consider leveraging Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions that provide multi-tenancy capabilities.
Compliance with regulations and data security are critical considerations when integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing. Ensure that your chosen cloud service provider adheres to industry standards and compliance requirements to protect sensitive data.
Cloud-based storage enables organizations to store and access data remotely. When integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing, ensure that your cloud storage solution offers adequate capacity, security, and remote access capabilities for seamless data handling.
Efficiently distributing workloads across multiple cloud servers helps achieve load balancing and high availability. Integrate load balancing mechanisms into your cloud computing infrastructure to ensure that resources are evenly distributed and accessible at all times.
Implementing disaster recovery strategies is crucial to protect your data and minimize downtime. Consider utilizing edge computing techniques, which process data closer to its source, to enhance your disaster recovery capabilities and reduce latency.
Integrating different data sources within your cloud-based computing environment is essential for efficient data management. Use data integration tools and combine various data sets in a central data warehouse for easy access and analysis.
Elastic scaling allows your infrastructure to automatically adjust resources based on demand to optimize performance and cost-efficiency. Integrate orchestration tools to automate scaling processes and ensure smooth operations as your computing needs fluctuate.
Consider integrating cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP), project management, and document management solutions to streamline business operations and enhance collaboration within your organization.
When integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing, leverage virtual machine technologies to efficiently utilize computing resources. Implement vulnerability scanning tools to proactively identify and address security vulnerabilities across your cloud infrastructure.
Utilize Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) solutions to simplify network management and enhance connectivity within your integrated cloud computing environment. Integrate accounting and resource management tools to monitor and optimize resource usage and costs.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively integrate cloud computing and cloud-based computing to maximize the benefits and optimize their operations.
Cloud-based computing integration has become crucial for businesses in various industries to enhance their operations and stay competitive. Several case studies exemplify successful integrations that have leveraged the power of cloud computing technologies.
A leading retail company integrated Data-as-a-Service (DaaS) into its operations to gain real-time insights about customer behavior and preferences. By utilizing the scalability and reliability of the cloud, the company was able to perform big data analytics on a vast amount of customer data collected from various sources. This integration helped the company tailor its marketing strategies and optimize inventory management to improve customer satisfaction and increase sales.
A manufacturing company integrated cloud-based computing into its supply chain management (SCM) processes. By connecting edge devices with cloud infrastructure, the company was able to collect and analyze real-time data from different stages of the manufacturing process. This integration improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enabled proactive maintenance by providing real-time insights into the production line. Additionally, the company used cloud-based CRM systems to enhance customer relationship management.
A gaming company successfully integrated cloud computing to revolutionize the gaming experience. By utilizing cloud-based architecture and data sovereignty, the company allowed gamers to seamlessly access and play games from any device, anywhere. This integration enabled multiplayer gaming and reduced the need for expensive gaming hardware. Cloud-based gaming also provided opportunities for developers to improve version control, automation, and DevOps practices, ensuring a smooth and immersive gaming experience for users.
An advertising agency integrated multiple cloud platforms to streamline its online marketing campaigns. By utilizing a multi-cloud approach, the agency could leverage the strengths of different cloud vendors and avoid vendor lock-in. This integration enabled efficient resource pooling and scalability, ensuring that the agency’s campaigns could handle high traffic volumes without compromising performance. Additionally, cloud-based edge analytics helped the agency analyze real-time data from various advertising channels, allowing for agile decision-making and optimization of marketing strategies.
In conclusion, these case studies highlight the diverse benefits and successful implementations of cloud-based computing integration in various industries. From retail to manufacturing, gaming to advertising, cloud computing technologies have paved the way for improved scalability, reliability, security, and efficiency. Businesses that embrace and effectively integrate cloud-based computing can gain a competitive edge, improve customer satisfaction, and drive innovation in their respective industries.
In the future, cloud computing integration and cloud-based computing integration will play a crucial role in various industries. One area that will benefit from this integration is document management. With cloud-based deployment and continuous deployment, companies can ensure that the latest versions of documents are always available, making version control more efficient and streamlined.
Data protection will also see significant improvements with cloud computing integration. By leveraging the expertise of cloud providers, companies can enhance their data protection measures and ensure the security of their sensitive information. Continuous development in the cloud will also enable companies to keep up with evolving human resources demands by providing flexible and scalable solutions.
Cost optimization will become a key consideration in cloud computing integration as companies seek to maximize their resources. With storage-as-a-service, companies can avoid large upfront costs and only pay for the storage they need. Mobile backup and finance applications will also benefit from cloud-based integration as companies can access data from anywhere, while ensuring its security through firewalls and other protective measures.
Data processing and analytics will also be enhanced with cloud computing integration. Companies can leverage the power of the cloud to perform advanced data mining, enabling them to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. Service reliability will also improve as cloud providers offer more robust and scalable solutions.
Hybrid integration will continue to gain momentum as companies combine private cloud and public cloud resources. This approach allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as well as increased security and control. Platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and software-as-a-service (SaaS) models will continue to evolve, providing companies with more options to integrate cloud-based solutions into their existing architecture.
Machine learning (ML) and big data will also play a significant role in future cloud computing integration. By leveraging the power of ML algorithms and analytics, companies can unlock valuable insights from their data and optimize their operations. This will be especially beneficial in industries such as retail, where data visualization and edge computing can provide innovative solutions for improving customer experience and increasing efficiency.
In summary, the future of cloud computing integration and cloud-based computing integration looks promising. The integration of various services and technologies will enable companies to optimize costs, improve data protection, enhance data processing and analytics, and leverage emerging technologies such as ML and big data. With continuous development and the evolution of cloud-based solutions, companies will have the tools they need to stay competitive in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
When integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing, there are several security considerations that need to be taken into account to ensure the protection of data and systems. One important aspect is data management, which involves securing data at rest and in transit, as well as implementing appropriate access controls to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive information. This includes implementing authentication mechanisms and identity and access management systems.
In addition to data management, security considerations also extend to the distributed nature of cloud and cloud-based computing. Distributed computing introduces challenges in terms of load balancing, high availability, and scalability. These aspects are crucial for ensuring that the resources and services are available and can handle increased demand as needed. Continuous deployment and continuous development processes should be implemented, along with automation and elastic scaling, to effectively manage and secure the distributed infrastructure.
Another important security consideration is the protection of sensitive business intelligence and intellectual property. Cloud-based computing offers various technologies and tools for managing and analyzing big data, including data mining and analytics. However, it is essential to ensure that the data privacy and governance policies are in place, especially when dealing with sensitive information in industries such as manufacturing, retail, and the Internet of Things.
Disaster recovery and backup strategies should also be implemented to safeguard against data loss and ensure business continuity. Managed services and server monitoring should be utilized to detect and respond to any potential security threats and vulnerabilities. Application programming interfaces (APIs) should be secured to prevent unauthorized access and attacks.
Overall, integrating cloud computing and cloud-based computing requires a comprehensive approach to security. It is crucial to consider various factors such as data privacy, authentication, distributed computing, scalability, and cost in order to ensure the protection of systems and data in the cloud environment.
Some security considerations in integrating cloud computing include data breaches, data loss, unauthorized access, and the security of the cloud provider’s infrastructure.
Data breaches can be prevented when integrating cloud computing by implementing strong authentication and access controls, encrypting sensitive data, regularly monitoring for suspicious activity, and keeping software and systems up to date.
The risks of data loss in cloud-based computing include hardware failure, software bugs, natural disasters, and human error. It is important to implement robust backup and disaster recovery strategies to mitigate these risks.
Unauthorized access can be prevented in cloud-based computing by implementing strong authentication mechanisms, regularly reviewing and updating access controls, and implementing security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
To ensure the security of the cloud provider’s infrastructure, it is important to conduct due diligence before selecting a provider, assess their security certifications and compliance with regulatory standards, and regularly monitor their security practices and incident response capabilities.
Some best practices for ensuring security when integrating cloud computing include educating employees about security risks, implementing strong password policies, regularly auditing access logs, encrypting sensitive data, and conducting regular security assessments and penetration testing.