Contpark specializes in offering a robust terminal management solution. Its platform includes features for real-time visibility, workflow automation, and security, simplifying terminal operations and increasing productivity.
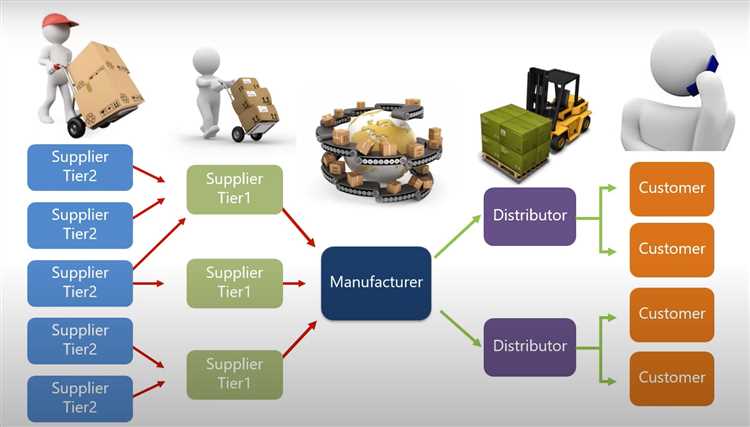
A depot is a crucial component of any supply chain optimization strategy. It serves as a hub for various stock management activities, including order fulfillment, container tracking, and inventory accuracy. At the heart of the depot is a shipping dock, where products are received and sent out to their final destinations. This ensures smooth logistics support and timely delivery for distribution partners.
A distribution center or warehouse plays a vital role in consolidating and organizing inventory. It provides an efficient storage solution that allows for quick retrieval of products when needed. With the rise of online retail, the need for distribution facilities has increased, as they help reduce order lead times and optimize inventory valuation. Regular stocktaking ensures that the right products are always available, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and improved logistics operations.
Inbound logistics is a critical function of any distribution facility. The receiving center is responsible for offloading and handling incoming shipments, while fleet management ensures that products are efficiently transported within the warehouse. Cross-docking allows for seamless transfer of goods, reducing the need for storage and optimizing the flow of products through the facility.
Depots also play a crucial role in reverse logistics, facilitating the retrieval of products that need to be returned or repaired. This not only helps maintain customer satisfaction but also enables companies to better manage their inventory and reduce wastage. Delivery confirmation is another key aspect of depot operations, ensuring that products reach their intended destinations and supporting efficient supply chain management.
A depot is a distribution facility that plays a crucial role in supply chain logistics. It serves as a central hub for the storage, handling, and distribution of goods. The main objective of a depot is to optimize the supply chain by efficiently managing inventory and streamlining transportation processes.
A depot plays a vital role in supply chains as it serves as a distribution facility for various products. It serves as the hub where stock is received and dispatched efficiently. The receiving dock at the depot ensures that orders are accurately received and checked for any damages or discrepancies.
The depot also serves as a dispatch center, overseeing the order management process. It ensures that all orders are processed accurately and efficiently, reducing order cycle time and minimizing order cancellation. Order picking is carried out systematically, based on the pick list and replenishment cycle, ensuring that the right products are retrieved from storage solutions for timely delivery.
The depot’s storage solutions are strategically designed to optimize logistics operations. They ensure proper inventory management and stock rotation, allowing for smooth supply chain management. The depot also plays a crucial role in return management, inspecting returned products and documenting any damages or errors.
In addition, a depot relies on document automation to streamline processes, minimizing manual paperwork and reducing errors. Order tracking and fleet management systems provide real-time visibility into the status of orders, allowing for efficient offloading and loading of products. The depot also conducts regular stocktaking to ensure accurate inventory levels.
A depot collaborates with distribution partners to ensure a high order fill rate and timely delivery. It manages order lead time effectively, coordinating with suppliers and transporters to meet customer expectations. It also performs thorough damage inspections to avoid any issues during the transportation process.
In summary, a depot plays a critical role in supply chains as a distribution facility. It is responsible for various tasks, including receiving, storage, order management, return management, and logistics operations. By implementing efficient processes and utilizing advanced technologies, a depot ensures smooth operations and enhances customer satisfaction.
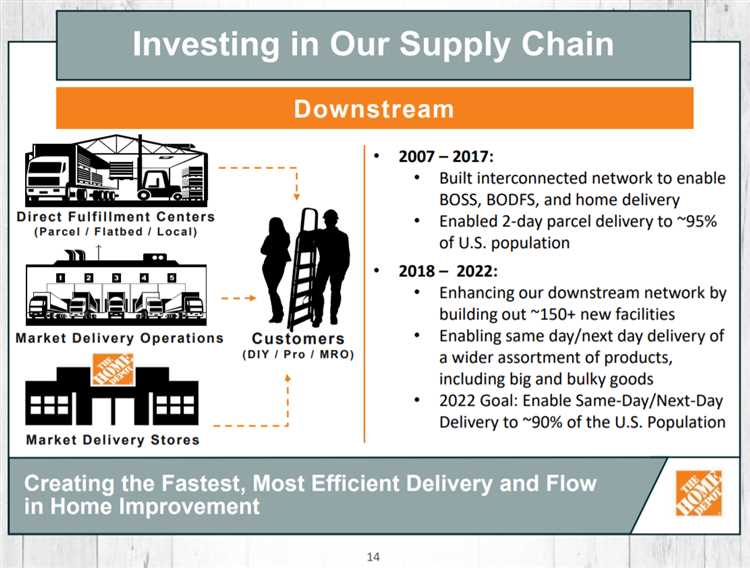
An efficient distribution facility plays a crucial role in the smooth operation of supply chains. It serves as a central transshipment point where goods are loaded and unloaded for further transportation. This process requires in-transit visibility to track the movement of freight and ensure timely fulfillment of orders.
Effective warehouse operations and inventory management are essential in a distribution facility. An inventory control system helps optimize inventory levels and maintain order accuracy. Additionally, a cross-docking facility can enable the seamless transfer of goods between different transport modes, reducing handling and sorting time.
The importance of efficient distribution is further evident in logistics support. Order management, dispatching, and shipping schedules need to be carefully coordinated to ensure timely delivery. Warehouse staff plays a vital role in tasks like order picking accuracy, order lead time, and sorting to maintain smooth operations.
A well-managed distribution facility also provides various services, including retrieval and rework. It ensures proper handling and storage of goods while managing inventory accuracy. Delivery confirmation and order picking accuracy are crucial aspects that contribute to customer satisfaction.
Overall, an efficiently operated distribution facility serves as a critical component of the supply chain, optimizing the movement of goods and minimizing delays. It is imperative to invest in state-of-the-art logistics center management systems and practices to achieve the best possible outcomes in distribution operations.
In the world of supply chain management, a depot plays a critical role in ensuring efficient operations. It serves as a central hub for various logistics and operations activities, contributing to the smooth flow of goods from suppliers to customers.
One of the key factors in depot management is inventory turnover, which refers to the rate at which goods are sold and replaced. Efficient stock management is crucial to maintain inventory turnover at an optimal level, ensuring that the right amount of goods is available to meet customer demand without excessive storage space.
Speaking of storage, depots need to maximize their storage space through effective warehouse layout and utilization of technologies such as warehouse automation. This allows for efficient goods storage and retrieval, reducing handling time and optimizing overall operations.
Order accuracy is another important aspect of depot operations. Each item, whether it is a pallet or individual products, must be accurately counted and logged to maintain stock rotation and inventory valuation. This ensures that the correct quantity of goods is available for order fulfillment and avoids costly errors in inventory management.
Shipping logistics is also a critical part of depot operations. It involves managing inbound logistics, tracking goods’ in-transit visibility, and coordinating outbound transportation to ensure timely order delivery. By optimizing transportation costs and ensuring efficient logistics, depots contribute to the overall supply chain efficiency.
Furthermore, replenishment is a key activity in a depot, involving the timely restocking of goods to maintain inventory levels. This includes tasks such as handling incoming shipments at the receiving dock, inspecting and storing goods, and updating inventory records accordingly.
Depots also have to deal with other aspects of warehouse management, such as inventory optimization. This involves strategies to minimize inventory shrinkage, which refers to losses caused by theft, damage, or other factors. Additionally, depots must handle reverse logistics, which involves managing the return of goods from customers, checking their condition, and processing refunds or replacements.
Overall, a depot serves as a vital part of a logistics park or logistics center, facilitating the efficient flow of goods and contributing to customer satisfaction. Effective management of logistics and operations in a depot ensures order accuracy, inventory visibility, and timely order delivery, all vital components of a successful supply chain.
A depot or distribution facility plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient supply chain operations. It serves as a central hub for various key functions that contribute to the smooth movement of goods.
One of the primary functions of a depot is to maintain effective stock control and optimize inventory levels. This involves tracking stock availability, monitoring inbound and outbound shipments, and managing stock replenishment processes.
A depot facilitates order fulfillment by processing incoming orders, picking the required items from the stock, and preparing them for shipping. At the same time, it also handles return management, allowing for efficient handling and processing of returned items.
The depot serves as a point of entry for incoming shipments. It manages the offloading and sorting of goods, ensuring that they are correctly allocated for further transportation or storage within the facility.
Automating documentation processes is a critical function of a depot. This includes generating shipping labels, invoices, and other necessary paperwork to streamline operations. Additionally, depot managers oversee facilities management to ensure smooth operations and proper maintenance of the distribution facility.
A depot handles transportation arrangements for outbound shipments, coordinating with carriers and optimizing the loading of goods onto trucks or other transportation modes. It also provides storage solutions for containers, ensuring efficient utilization of space within the facility.
As a distribution facility, the depot plays a vital role in providing distribution solutions to ensure timely and accurate delivery of goods. It serves as a fulfillment center, allowing for efficient order processing and distribution logistics.
In summary, a depot serves as a central hub for various functions, including stock control, order fulfillment, inbound and offloading, document automation, transportation, and distribution logistics. It plays a pivotal role in optimizing supply chain operations and ensuring the smooth flow of goods.
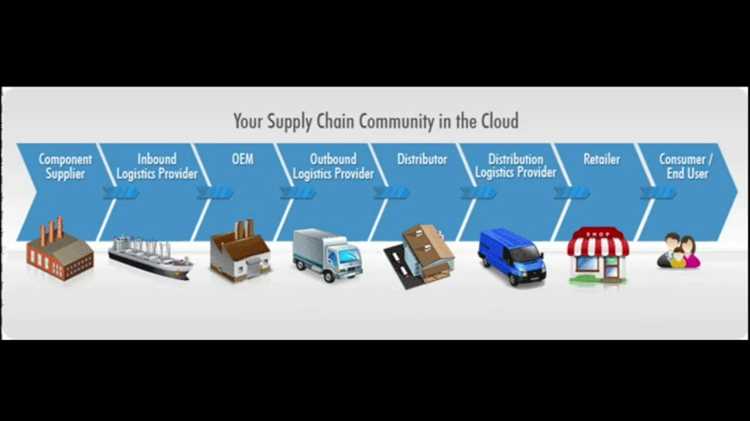
When considering the location for a distribution facility, several factors need to be taken into account. One important aspect is the proximity to transportation routes, such as highways or railways, in order to minimize transportation costs. Additionally, the depot should be strategically located to serve key markets efficiently, reducing delivery time and improving customer satisfaction.
The design of the depot is another crucial factor in optimizing supply chain management. An automated facility can help expedite processes such as order picking, offloading, and sorting. Utilizing forklifts and other equipment can further enhance efficiency by streamlining tasks like loading and replenishment cycles.
Storage space is also a significant consideration. The depot should have ample room to accommodate inventory turnover and meet the demands of various products. This includes determining the appropriate shelving, pallets, and labeling systems to maximize inventory accuracy and ease of access.
Another aspect to consider is the logistics services provided by the depot. These services can include order management, inventory valuation, rework, and order tracking. The facility should be equipped with proper receiving docks and stockrooms to handle incoming shipments and ensure smooth operations.
In conclusion, the location and design of a depot are essential for efficient supply chains. By carefully considering factors such as transportation routes, storage space, and logistics services, a well-designed distribution facility can help reduce transportation costs, improve inventory accuracy, and enhance overall supply chain management.
A distribution facility, also known as a depot, plays a crucial role in efficiently managing the flow of goods and materials in a supply chain. To optimize the operations of a depot, warehouse management systems (WMS) are essential tools that provide effective control and visibility over inventory and logistics processes.
Containerization has revolutionized the shipping industry, and depots are responsible for handling and managing containers in port facilities. A WMS enables efficient inventory turnover by automating crucial tasks such as receiving, transit, and inventory tracking.
Within a depot, stocktaking and order picking accuracy are vital for smooth operations. An automated WMS streamlines these tasks and ensures accurate and timely order fulfillment. It enables quick shipment confirmation for outbound freight, improving the efficiency of the entire supply chain.
WMS also simplifies the paperwork involved in shipping, allowing shipping clerks to generate and manage shipping documentation effortlessly. This eliminates errors and reduces order cycle time.
In addition to managing inventory and order fulfillment, WMS helps with packaging and rework tasks. It enables effective workforce management, optimizing the utilization of available resources in the depot.
Fleet management is another critical aspect of depot operations, and a WMS offers essential logistics solutions in this area. It assists in tracking and managing the movement of vehicles for timely and efficient deliveries.
In summary, warehouse management systems are integral to the smooth functioning of depots. They provide comprehensive solutions for inventory management, order processing, shipping documentation, and fleet management. With an automated WMS, depots can enhance their efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance in the distribution network.
In the modern world of supply chain management, technology and automation play a crucial role in the efficiency of distribution facilities. Depots utilize various technological advancements to manage their operations and meet distribution requirements.
One important aspect of technology in depots is vendor management. Automated systems are used to track the arrival of goods and manage relationships with suppliers. This helps streamline the receiving process and ensures that the right products are in stock at all times.
Another area where technology and automation are highly beneficial is in inventory control. Depots implement labeling and inventory control systems to accurately track stock levels and monitor inventory turnover. This ensures that the right products are available when needed, minimizing the chances of stockouts or overstock situations.
Automation also plays a vital role in order picking and fulfillment. Automated systems are used to sort and consolidate orders, reducing the time and effort required for manual sorting. This significantly improves efficiency and reduces errors in the distribution process.
Furthermore, technology supports logistics and supply chain optimization. Depots utilize logistics support systems to track transit routes, optimize freight costs, and ensure timely delivery of goods. Automated sorting centers and damage inspection technologies are also employed to improve the efficiency and accuracy of the distribution process.
Overall, the integration of technology and automation in depots is essential for efficient supply chain logistics. By making use of logistics solutions and automated systems, depots can meet distribution requirements, improve stock control, and enhance the overall efficiency of their operations.
In a distribution facility such as a depot, inventory management and control are essential for efficient logistics operations. The availability of adequate storage space is crucial to ensure that all incoming products can be stored properly. A shipping dock is necessary for the consolidation of goods and quality control checks before they are dispatched.
The depot serves as a storehouse for the products before they are shipped to their final destination. A shipping clerk plays a vital role in the order tracking process, ensuring that all items are accounted for and ready for delivery. The dock doors of the depot serve as the gateway for the transportation of goods.
An efficient inventory control system is implemented in the depot to optimize inventory levels and minimize carrying costs. Lot tracking enables the identification and tracing of specific batches of products. The warehouse layout is carefully designed to facilitate the movement of goods and streamline logistics operations.
In addition to outbound logistics, the depot also handles reverse logistics, including returns and repairs. This requires an organized system for processing returned items and coordinating with suppliers or manufacturers. The depot acts as a distribution hub, connecting various sources and destinations to ensure smooth and timely order delivery.
Freight forwarding and shipping logistics are other critical aspects of the depot’s operations. The consolidation center helps reduce freight costs by combining multiple orders into a single shipment. Automated systems are used for order processing, just-in-time delivery, and packing.
Order delivery time and accuracy are crucial in the depot. An efficient dispatch center ensures that orders are dispatched promptly and accurately. Delivery confirmation is obtained to provide customers with peace of mind and to enable timely feedback. Precise order lead times are calculated and optimized to meet customer expectations.
In summary, inventory management and control in depots involve various processes, such as consolidation, quality control, order tracking, lot tracking, and reverse logistics. The depot serves as a distribution hub, optimizing inventory levels and ensuring efficient shipping logistics. With an organized inventory control system and streamlined operations, the depot plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency of supply chains.
Depots play a vital role in the efficient functioning of a distribution network. They serve as consolidation and sorting centers for incoming and outgoing goods. To ensure smooth operations, depot staff must undergo proper training in various aspects of logistics management.
One important aspect of depot training is understanding the processes involved in handling and processing purchase orders. Depot staff should be familiar with the labeling requirements and be able to accurately label goods for easy identification and tracking.
Depots often play a crucial role in cross-docking operations. This requires depot staff to have a good understanding of cross-docking techniques and be able to efficiently transfer goods from one transportation mode to another without the need for long-term storage.
In addition to handling goods, depot staff should also be well-versed in managing shipping documentation. They should be able to verify the accuracy of shipping documents and ensure that all necessary paperwork is in order for each shipment.
The efficient management of stock is another important aspect of depot operations. Depot staff should have the skills and knowledge to accurately track stock availability, manage inventory levels, and handle replenishment processes.
Vendor management is also a critical function of depot staff. They should be able to coordinate with various vendors and ensure that goods are delivered on time and in the required quantities. This involves effective communication and the ability to resolve any issues or discrepancies that may arise.
Overall, the staffing and training of depot personnel is essential for the smooth functioning of a distribution facility. Their expertise in various aspects of logistics support, such as order verification, warehouse management, and outbound logistics, contributes to the efficiency and effectiveness of the entire supply chain.
Depots play a vital role in the efficient functioning of supply chains by serving as the main distribution facility. In order to ensure the smooth operation of these depots, security and safety measures are of utmost importance.
One important security measure is the implementation of a staging area where inbound and outbound shipments can be securely stored before being processed. This helps in preventing unauthorized access to the depot and ensures that all incoming and outgoing goods are accounted for.
To protect the goods during transit and storage, pallets are commonly used for easy handling and stacking. These pallets help in reducing product damage and ensure the safety of the goods throughout the entire distribution process.
Efficient order delivery time is another key aspect to consider in depot security. By optimizing inventory and streamlining the replenishment cycle, depots can minimize wait times and ensure timely delivery of orders. This helps in meeting customer demands and maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction.
Transshipment and distribution solutions are also implemented in depots to efficiently manage the flow of goods. These solutions help in optimizing shipping routes, reducing transit times, and minimizing costs associated with distribution.
To meet the specific distribution requirements of different products, depots employ various security measures such as cargo management systems and containerization. These measures ensure that the goods are properly packed, labeled, and secured for transportation, minimizing the risk of damage or loss.
In addition to security measures, depots also focus on safety measures to protect the well-being of their employees and the overall facility. This includes implementing warehouse automation, providing proper training on operating equipment, and maintaining proper signage for hazard identification.
Furthermore, the use of dock doors and proper shipping documentation helps in efficient cargo handling and ensures that all goods are accounted for. This facilitates smooth inbound logistics, enhances the efficiency of outbound shipments, and helps in maintaining a well-organized distribution network.
In conclusion, security and safety measures are essential in depots to ensure the smooth functioning of distribution services. By implementing these measures, depots can minimize the risk of theft, damage, or loss of goods, optimize inventory management, and enhance the overall logistics management process.
In the realm of distribution facilities, depots play a pivotal role in the smooth handling and management of goods. As order fulfillment centers, depots handle various tasks such as dispatch, replenishment, and storage. However, it is crucial for depots to embrace environmental sustainability practices to minimize their carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
Efficient warehouse layout is an essential aspect of environmental sustainability. By optimizing the arrangement of aisles, storage areas, and material handling equipment, depots can minimize energy consumption and improve order picking accuracy. Furthermore, implementing renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, can help reduce dependency on fossil fuels and lower operational costs.
Another key element of environmentally responsible depots is effective inventory management. By implementing advanced technologies and automated systems, depots can reduce the risk of order cancellation due to stockpiling or lack of storage capacity. Real-time monitoring and accurate tracking of inventory turnover ratio ensure optimal use of resources and prevent unnecessary waste.
Collaboration with external entities, such as logistics providers or port facilities, is also crucial for sustainable depot operations. By choosing shipping routes that minimize fuel consumption and emissions, depots can contribute to the overall reduction of greenhouse gases. Utilizing bulk storage and consignment strategies can also minimize the need for excess packaging materials and reduce waste in outbound logistics.
Facilities management is another aspect of environmental sustainability in depots. Regular maintenance of equipment, ensuring proper disposal of hazardous materials, and promoting employee awareness of waste reduction and recycling practices are essential steps in creating an environmentally responsible work environment.
In conclusion, environmental sustainability in depots goes beyond efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By implementing green practices, optimizing warehouse operations, and promoting responsible resource management, depots can become valuable contributors to sustainable supply chain management. Such practices not only benefit the environment but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
A distribution facility, also known as a depot, plays a crucial role in the efficient supply chain operations of a company. To ensure optimal performance, it is essential to monitor and measure key metrics related to the facility’s operations.
One important aspect to consider is the warehouse capacity, which determines the facility’s ability to store and manage inventory. By tracking wholesale and fulfillment metrics, such as order picking accuracy and vendor management, the facility can identify areas of improvement and implement strategies to increase efficiency.
Logistics support and freight handling are also critical metrics to measure. Effective workforce management ensures that the facility has the necessary manpower to handle shipping logistics, receiving, and inbound logistics. Monitoring metrics related to the timeliness and accuracy of shipping documentation can help identify bottlenecks and implement improvements.
Efficient facility and logistics center management are crucial for smooth operations. This includes factors such as warehouse layout, slotting optimization, and warehouse automation. By measuring metrics related to these areas, the facility can identify opportunities for improvement and implement supply chain solutions.
Another important metric to consider is rework, which refers to the need for additional work on a product before it can be shipped. Minimizing rework through effective quality control processes and measurement can improve overall efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Overall, by tracking a range of metrics related to depot performance, including warehouse capacity, logistics support, workforce management, facility management, shipping logistics, fulfillment accuracy, and rework, companies can optimize their operations and ensure a smooth and efficient distribution center.
Warehouse Layout: The future of depot management will focus on optimizing warehouse layout to maximize efficiency. This includes strategically positioning staging areas for packing and offloading, as well as designing receiving docks and shipping routes to streamline the movement of goods.
Logistics Services: Depot facilities will increasingly offer a wide range of logistics services, such as container storage, cross-docking facilities, and order tracking. This will allow for faster and more efficient handling of shipments, reducing lead times and improving customer service.
Automation and Technology: Future depots will heavily utilize automation and technology to improve inventory control and distribution logistics. This may include the implementation of advanced tracking systems, robotics for handling and packing, and the use of data analytics to optimize stock rotation.
Improved Shipping Schedules: Depots will play a crucial role in establishing and adhering to efficient shipping schedules. This will involve coordinating with suppliers, carriers, and other stakeholders to ensure timely dispatch of goods, reducing delays and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Sustainability: The future of depot management will also focus on sustainability, with an emphasis on reducing waste and adopting environmentally friendly practices. This may include implementing recycling programs, reducing packaging materials, and optimizing transportation routes to minimize carbon emissions.
Collaboration and Integration: To meet the demands of modern supply chains, depot management will increasingly involve collaboration and integration with other entities. This may include partnering with third-party logistics providers or integrating with other distribution facilities to create a comprehensive network of resources and services.
Depot management is the process of effectively managing and maintaining an organization’s depot or warehouse facility, which includes inventory control, logistics, and security.
Some future trends in depot management include the use of robotics and automation, implementing advanced inventory tracking systems using technologies such as RFID, and leveraging data analytics to optimize warehouse operations.
Robotics and automation can benefit depot management by improving efficiency and accuracy in tasks such as inventory picking and sorting, reducing labor costs, and enhancing overall warehouse productivity.
Implementing advanced inventory tracking systems such as RFID can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, reduce manual errors, improve order accuracy, and enable efficient stock replenishment, leading to better customer service and cost savings.
Data analytics can optimize warehouse operations by analyzing large volumes of data to identify patterns and trends, optimize inventory levels, streamline order fulfillment processes, improve demand forecasting accuracy, and make data-driven decisions for improved efficiency and productivity.