Contpark specializes in offering a robust terminal management solution. Its platform includes features for real-time visibility, workflow automation, and security, simplifying terminal operations and increasing productivity.
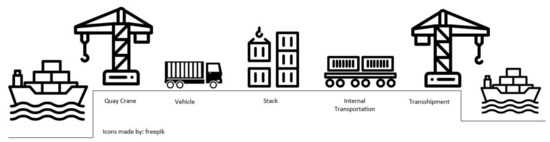
In today’s global logistics industry, an efficient and well-organized transshipment system plays a crucial role in streamlining the interchange of goods. The transshipment system involves various key processes, such as logistics network management, load planning, container logistics, and last mile delivery, which collectively ensure a smooth flow of goods from the point of origin to the final destination.
One of the essential components of a transshipment system is the port, which serves as a major hub for handling the exchange of containers between different modes of transportation. At the port, containers are unloaded from ships and loaded onto trucks or trains for further transportation. This process requires coordination between shipping clerks, dock workers, and other logistics personnel to ensure the efficient handling and exchange of containers.
Another important aspect of the transshipment system is supply chain integration. By integrating various elements of the supply chain, including warehousing, storage and distribution, and freight logistics, a seamless flow of goods can be achieved. This integration allows for better coordination and planning of logistics operations, leading to improved efficiency and reduced freight costs.
Containerizing goods is another key practice in the transshipment system. By packaging goods into containers, they can be easily transported and handled throughout the entire logistics network. This containerization process enables efficient conveyancing of goods from one point to another, regardless of the mode of transport used.
Overall, an effective transshipment system is crucial for optimizing the exchange of goods in the logistics industry. It ensures smooth logistics operations, reduces costs, and enhances customer satisfaction by delivering goods in a timely and reliable manner. By streamlining the interchange of goods, the transshipment system plays a vital role in the global supply chain and contributes to the overall success of businesses involved in international trade.
A transshipment system plays a crucial role in facilitating the interchange of goods in today’s global trade. It provides a seamless process for the selling, purchase, and transfer of goods between various trading partners. One of the key advantages of a transshipment system is its ability to simplify freight transportation by optimizing the logistics management system. By using route optimization techniques, it ensures that goods are efficiently transported from one point to another, whether by ship, trucking, or cargo transportation.
In addition to optimizing the delivery route, a transshipment system also enables efficient inventory tracking and management. With the help of advanced technology, it allows for real-time monitoring of inventory levels, ensuring that goods are stored and transferred in a timely manner. This not only improves supply chain coordination but also helps in minimizing inventory costs and avoiding stockouts.
Another benefit of a transshipment system is its ability to streamline the packaging and containerizing process. It provides a centralized platform where goods can be appropriately packaged and transferred to containers, ensuring their safety and integrity during transportation. Furthermore, it enables efficient stowage, maximizing the use of space in containers and reducing the risk of damage or loss of goods.
Furthermore, a transshipment system plays a critical role in supply chain optimization. It facilitates the smooth flow of goods from the point of origin to the distribution center, minimizing delays and improving overall efficiency. Additionally, it enables effective logistics management by transmitting relevant information regarding the status and location of goods, enabling timely decisions regarding their transfer and further handling.
Overall, a well-implemented transshipment system is essential for the smooth functioning of the logistics industry. It simplifies the process of carrying, transporting, and delivering goods, ensuring that they reach their intended destinations in a timely and cost-effective manner. By optimizing supply chain processes, it enhances overall supply chain efficiency and supports the growth of global trade.
Transshipment plays a vital role in the smooth interchange of goods within the supply chain. It involves the movement of goods from one mode of transportation to another without being stored in a warehouse. This practice allows for more efficient supply chain optimization as it reduces the need for warehousing and storage, minimizing the time it takes for goods to reach their final destination.
Third-party logistics companies often play a significant role in transshipment. They act as intermediaries and coordinate the transportation operations between different carriers. These logistics providers ensure that the goods are handled, packaged, and transported appropriately during the transshipment process, optimizing the flow of goods and reducing the risk of damage or loss.
The logistics optimization in transshipment is a coordinated effort among various parties involved. Logistician professionals oversee the carrying, handling, transporting, and exchanging of goods, ensuring that the entire supply chain remains synchronized and efficient. This coordination includes the selection of transportation services, such as trucking or trans-freight, to ensure the proper movement of goods from one point to another.
Transshipment also plays a crucial role in reverse logistics. It allows for the efficient management of returned goods, providing a seamless process for storage and distribution. Automated warehouses and transportation management systems enable the quick and accurate processing of goods, reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Overall, transshipment is a critical component of the supply chain that facilitates the smooth and efficient interchange of goods. It enables supply chain coordination and optimization, ensuring that goods are transported quickly and safely from the point of origin to their final destination. By minimizing the need for warehousing and streamlining the logistics system, transshipment plays a crucial role in supply chain management and enhances the overall efficiency of the interchange of goods.
Efficient transshipment plays a crucial role in reducing costs and enhancing the interchange of goods within the supply chain. By streamlining supply chain planning, handling, and integration, companies can optimize their logistics management system to minimize unnecessary expenditures.
Through effective forwarding and conveyancing strategies, goods can be efficiently transported between different locations, such as warehouses or distribution centers. Utilizing a shuttle system can expedite the flow of transactions, saving time and reducing expenses in outbound logistics.
Transloading, or transferring goods from one mode of transportation to another, is another method that can lead to cost savings. By utilizing automated warehouses and efficient inventory control, companies can minimize the time and labor involved in packing, distribution, and transportation. This optimization of the supply chain can also improve the overall coordination and stowage of goods, further increasing efficiency.
In addition, trans-freight, or the transfer of goods between different carriers or modes of transportation, can reduce costs by utilizing the most cost-effective shipping options. This allows for the optimization of the transportation network and enables companies to make informed decisions regarding the most efficient routes and methods of conveyance.
Overall, the efficient transshipment of goods within the supply chain can lead to significant cost savings. By focusing on supply chain optimization, coordination, and integration, companies can enhance their inventory management, purchasing, and overall supply chain efficiency. This ultimately results in a streamlined interchange of goods and reduced expenses throughout the entire supply chain process.
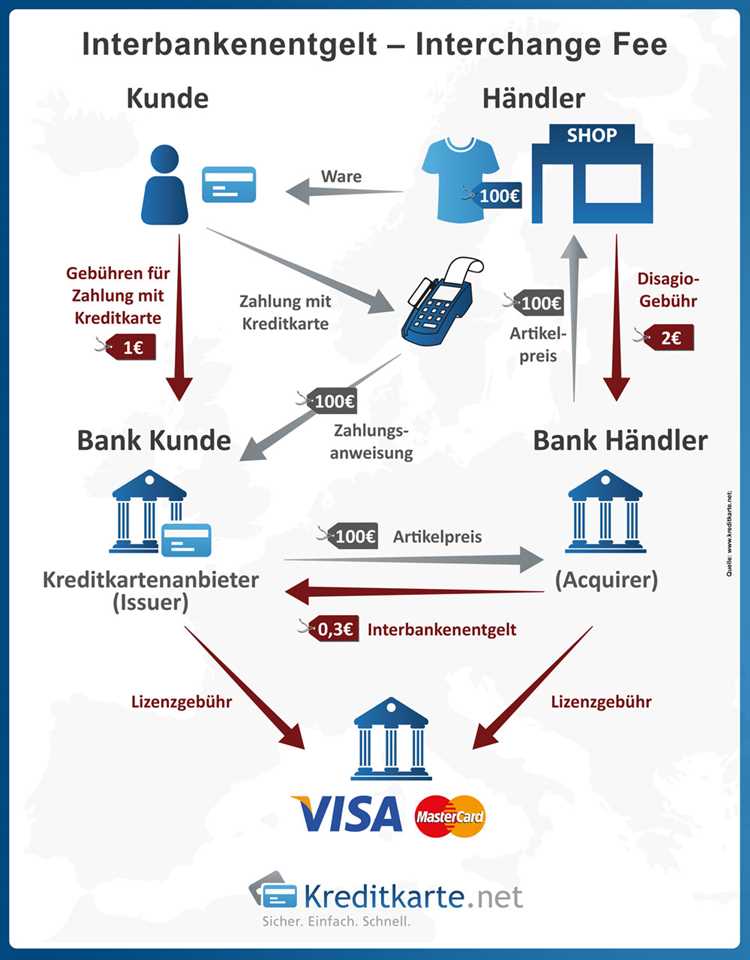
In the logistics industry, a transshipment system plays a crucial role in optimizing routes and managing inventory. It involves the process of packing and transferring goods from one mode of transport to another, often facilitated by a freight forwarder. This interchange of goods enables efficient trade and ensures smooth transportation logistics.
When goods arrive at a landing stage, the first step in the transshipment process is unloading and receiving them. To streamline the last mile delivery, the goods are containerized for easy handling and transportation. This approach allows for efficient interchange between different modes of transport, such as transferring goods from a ship to a truck.
A transshipment system also involves the use of logistics solutions and technologies. For instance, an automated warehouse can help in managing inventory turnover and ensuring timely supply chain integration. Additionally, intermodal transportation and a robust logistics infrastructure are critical components of a transshipment system.
In summary, a transshipment system is an essential part of the logistics industry, facilitating the efficient transfer and interchange of goods. It involves various processes such as loading, unloading, packing, and containerizing. With the help of freight forwarders and logistic companies, this system streamlines the transportation of goods and helps in route optimization. By utilizing logistics solutions and technologies, the transshipment system aids in inventory management and ensures smooth cargo transportation.
A transshipment system is an essential component of the supply chain and logistics infrastructure, facilitating the smooth interchange of goods between different modes of transportation and locations. It involves the coordination of various activities such as haulage, transportation operations, inventory management, fulfillment, and inventory control.
The primary purpose of a transshipment system is to enable efficient product distribution, trade, and importation by providing logistics support for the movement of goods. It ensures that goods are properly packed, handled, and transferred from one network to another, optimizing the transportation and logistics processes.
One of the key elements of a transshipment system is the last mile delivery, which focuses on the shipping logistics and ensuring the timely and accurate delivery of goods to their final destination. This involves inventory tracking, distribution center management, handling, unloading, and utilizing technologies such as ethernet switches and logistics management systems.
In summary, a transshipment system plays a crucial role in the smooth interchange of goods, providing the necessary infrastructure and processes for the efficient transferring of cargo between different modes of transportation, hubs, and logistic networks. Logistics managers rely on the transshipment system to ensure the seamless flow of goods and to optimize the overall logistics operations.
A transshipment system involves various key components that facilitate the efficient interchange of goods. These components include:
A transshipment system is a crucial component in the logistics industry that facilitates the smooth interchange of goods between different modes of transportation. This system plays a pivotal role in streamlining the movement of import and export goods, ensuring efficient delivery from origin to the final destination.
One of the main advantages of a transshipment system is its ability to optimize container logistics. By efficiently transferring containers between different modes of transportation, such as ships and trucks, the system significantly reduces the time and costs associated with long-haul trucking. A trucking company can utilize this system to seamlessly move goods from a port to a warehouse or distribution center, minimizing delays and enhancing overall efficiency.
Forwarding and logistics companies also benefit from a transshipment system. They can leverage this system to consolidate multiple shipments into larger containers, optimizing load planning and reducing the number of trucks required for delivery. By doing so, they can improve the efficiency of outbound logistics, lower freight rates, and reduce carbon emissions.
In addition to improving the efficiency of transportation operations, a transshipment system also enhances the last mile delivery process. By strategically locating transshipment hubs near major consumer areas, logistics managers can minimize the distance between the hub and the final delivery destination. This allows for quicker and more cost-effective delivery, making the system an indispensable tool in the distribution and fulfillment process.
The role of a transshipment system goes beyond the physical movement of goods. It also involves essential logistics support functions, such as warehousing, material handling, and stockpiling. For example, a freight forwarding company can utilize transloading services at a transshipment hub to efficiently transfer goods from one mode of transportation to another. This eliminates the need for intermediate warehousing and reduces the risk of inventory obsolescence.
In conclusion, the implementation of a transshipment system is crucial for streamlining the interchange of goods in the logistics industry. It optimizes container logistics, enhances outbound logistics, improves last mile delivery, and provides essential logistics support functions. With its ability to efficiently transfer goods between different modes of transportation, a transshipment system is a fundamental element of a robust logistics infrastructure.

The automation and digitization of transshipment processes have revolutionized the interchange of goods in distribution logistics and cross-border transportation operations. Through the use of advanced technology, such as automated conveying systems and inventory tracking software, the loading and receiving of goods have become more efficient and streamlined. Logistician now have access to real-time data, allowing for improved supply chain coordination and load planning.
One essential digitized process is cross-docking, where goods are unloaded from inbound transportation and immediately loaded onto outbound transportation without the need for warehousing. This eliminates the need for storage and distribution, reducing the time required for goods to circulate within the supply chain. Additionally, the use of containers and pallets has improved the efficiency of goods transportation, enabling easier handling and minimizing the risk of damage.
Automation and digitization have also enhanced supply chain planning and management. Logistics management systems can now track the movement of goods from the point of origin to the final destination, providing timely updates on the status of shipments. This not only improves customer satisfaction through more accurate delivery estimates but also allows for better supply chain optimization.
Inbound logistics have also been greatly simplified through automation and digitization. The use of advanced technology in receiving processes allows for faster and more accurate verification of goods, reducing the potential for errors and delays. This, coupled with efficient transportation services, ensures that goods flow smoothly through transit hubs, facilitating the efficient exportation and distribution of goods.
In conclusion, automation and digitization have transformed the interchange of goods in transshipment systems. These advancements have improved logistics support, such as inventory tracking and load planning, and have streamlined the loading, receiving, and distribution of goods. The efficient management of the supply chain, coupled with the use of containers and pallets, has created a seamless process that enhances the overall transit of goods and improves supply chain coordination.
Rapid advancements in technology have greatly impacted the efficiency and effectiveness of transshipment operations, enabling a streamlined interchange of goods. The integration of advanced technologies has revolutionized various aspects of transshipment management, including importation, inventory tracking, logistics management systems, and automated warehousing.
At the core of these advancements is the use of sophisticated logistics systems that facilitate the seamless flow of goods through the transshipment network. These systems efficiently manage the transfer, handling, and fulfillment of goods, minimizing errors and delays in the process. Real-time tracking and inventory turnover monitoring further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of transshipment operations, ensuring optimal utilization of resources.
An essential component of this integration is the use of automated warehouses, which have become a critical element in transshipment operations. These technologically advanced facilities utilize robotics and advanced material handling systems to optimize the storage, packing, and dispatch of goods. The integration of these automated processes not only reduces human error but also enhances the speed and precision of operations, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced freight costs.
The integration of advanced technologies also extends to the transportation phase of transshipment. Containerization has become a widely adopted practice in the industry, enabling standardized packaging and more efficient handling and transfer of goods. Additionally, the use of advanced logistics networks and delivery routes powered by GPS technology ensures optimal routes and timely deliveries.
In conclusion, the integration of advanced technologies in transshipment operations has significantly improved the interchange of goods, streamlining the importation, management, and distribution processes. From automated warehouses to real-time inventory tracking and optimized logistics networks, these advancements have revolutionized the transshipment industry, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving overall customer satisfaction.
A transshipment system offers numerous benefits for the interchange of goods, making it a valuable asset for businesses involved in export and import. Efficient management of shipping and conveying is crucial for successful product distribution, and a transshipment system simplifies the process.
One of the primary advantages of implementing a transshipment system is the optimized logistics planning it provides. The system enables businesses to strategically plan the transportation network, ensuring that goods are efficiently transported from suppliers to the final destination. This streamlined process minimizes transportation costs and enhances the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
Another benefit of a transshipment system is the consolidation of cargo. By utilizing a central hub for warehousing and distribution, multiple consignments can be combined into a single shipment. This not only reduces transportation costs but also simplifies the handling and packaging process. Furthermore, the system allows for load planning optimization, ensuring that containers are efficiently filled, maximizing the use of available space.
Implementing a transshipment system also enables businesses to leverage third-party logistics services. By outsourcing certain aspects of the shipping logistics, such as handling and transportation, businesses can focus on their core competencies, such as purchasing and product distribution. This leads to improved operational efficiency and cost savings, as companies can benefit from the expertise and resources of specialized logistics providers.
In addition, a transshipment system facilitates the exchange of goods between different modes of transportation. This flexibility allows for seamless intermodal transportation, with goods easily transitioning from one mode, such as trucks, to another, such as container shipping. This eliminates the need for unnecessary intermediate handling and reduces the risk of damage to the goods.
Overall, implementing a transshipment system provides businesses with a range of benefits, including improved logistics planning, cost savings, cargo consolidation, and seamless intermodal transportation. By optimizing the interchange of goods, companies can enhance their productivity and competitiveness in the global market.
The development of intermodal transportation has greatly improved the efficiency of logistics and supply chain management in the interchange of goods. With the help of freight forwarders and transportation and logistics companies, the process of coordinating the movement of goods has become more streamlined. Logistics managers have the ability to optimize inventory management and minimize the costs associated with transportation and distribution.
One key factor in improving efficiency is containerization. By packaging goods in standardized and stackable containers, it becomes easier to transport and handle them. These containers can be efficiently loaded and unloaded at distribution centers, reducing the time and effort required for handling and storage. This not only speeds up the shipment process but also minimizes the risk of damage during transportation.
To ensure smooth operations, a well-connected logistics network should be established. This involves collaboration between various stakeholders such as trucking companies, freight forwarders, and logistics managers. Efficient route planning and exportation strategies play a crucial role in timely delivery. Transactions between different hubs can be facilitated using conveyancing systems and load planning software to optimize storage and transportation.
The coordination of supply chain activities is essential for fulfilling customer demands. Fulfillment centers, shipping clerks, and supply chain coordinators work together to ensure that goods are delivered in a timely manner. By utilizing the latest transport logistics tools, such as ethernet switches, real-time information can be shared and analyzed to make data-driven decisions for effective supply chain management.
In conclusion, the implementation of intermodal transportation and improved logistics and supply chain efficiency has revolutionized the interchange of goods. Through containerization, optimized transportation routes, and a well-connected logistics network, companies can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. With the help of advanced technologies and efficient management strategies, the movement and carrying of goods have become faster and more reliable, leading to a more efficient supply chain system.
Logistics refers to the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient flow and storage of goods, services, and information from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
Logistics is important because it ensures the timely delivery of goods and services to customers. It helps in minimizing costs, optimizing resources, and improving customer satisfaction.
Supply chain efficiency refers to the ability of a supply chain to deliver products or services to customers with the minimum amount of resources and time. It involves optimizing all activities and processes within the supply chain.
Logistics can improve supply chain efficiency by streamlining transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and information flow. It focuses on reducing lead times, reducing costs, and improving overall operational performance.
Some benefits of improved logistics and supply chain efficiency include cost reductions, faster delivery times, improved customer service, increased productivity, better inventory management, and enhanced overall competitiveness.
Various technologies can help improve logistics and supply chain efficiency, such as transportation management systems, warehouse management systems, inventory management software, real-time tracking systems, data analytics, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices.