Contpark specializes in offering a robust terminal management solution. Its platform includes features for real-time visibility, workflow automation, and security, simplifying terminal operations and increasing productivity.
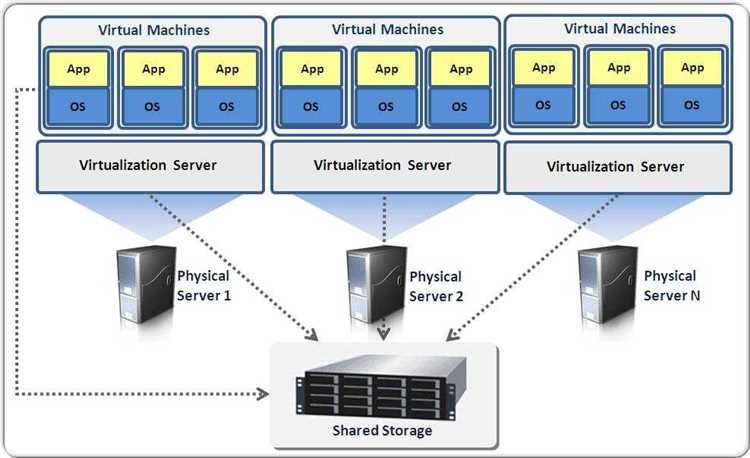
In today’s highly advanced technological world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to optimize performance, increase efficiency, and reduce costs. One technology that has gained significant prominence in recent years is host-based virtualization. Host-based virtualization is a powerful tool that enables businesses to create multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, thereby maximizing resource utilization and improving overall productivity.
At the heart of host-based virtualization is the virtualization platform, which provides the necessary environment for running multiple VMs. Virtualization platforms come in various models and mechanisms, each offering different levels of performance optimization and resource management capabilities.
One key aspect of host-based virtualization is its ability to partition resources such as CPU, memory, network, and storage among different VMs. This enables businesses to allocate resources based on the specific needs of each virtual workload, ensuring optimal performance and efficient resource utilization. Additionally, host-based virtualization allows for easy testing and business continuity, as VMs can be easily duplicated, backed up, and restored in case of any failures.
Furthermore, host-based virtualization also provides businesses with the flexibility to choose from a variety of virtualization tools, each offering different features and capabilities. These tools, combined with the use of virtualization standards such as SR-IOV, enable businesses to create a robust and scalable virtualization architecture that meets their specific needs.
However, it is important to note that while host-based virtualization offers numerous benefits, there are also considerations that need to be taken into account. One such consideration is the cost associated with virtualization, including both the initial investment in hardware and software, as well as the ongoing maintenance and support costs. Additionally, businesses also need to carefully plan and implement their virtualization strategy to ensure that it aligns with their overall IT goals and objectives.
In summary, host-based virtualization is a powerful technology that allows businesses to create and manage virtual machines on a single physical server. By leveraging various virtualization mechanisms and tools, businesses can optimize performance, improve resource utilization, and reduce costs. However, it is crucial for businesses to carefully plan and implement their virtualization strategy to ensure the desired outcomes are achieved.
Host-based virtualization is a powerful technology that enables the virtualization of servers within a data center. By utilizing a hypervisor, which is a software layer that sits between the host server’s hardware and the virtual machines, host-based virtualization enables multiple virtual machines to run simultaneously on a single physical server.
One of the key advantages of host-based virtualization is the ability to consolidate multiple servers onto a single physical server, leading to improved resource utilization and cost savings. This consolidation also simplifies backup and disaster recovery processes, as virtual machines can easily be replicated and moved between physical hosts.
There are different types of host-based virtualization technologies available, such as the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) and paravirtualization. These technologies provide flexibility in deploying and managing virtual machines, allowing for scalable architectures and easy live migration of virtual machines between hosts without disrupting service.
Host-based virtualization is also a key component of cloud computing, enabling organizations to build and manage virtual data centers that can be scaled up or down as needed. This microservices-based approach to computing offers increased agility and business continuity by isolating applications and services within individual virtual environments.
Additionally, host-based virtualization provides enhanced data protection capabilities, as virtual machines and their associated data can be easily backed up and restored. It also enables organizations to implement green computing practices by consolidating servers and reducing the overall energy consumption of their data centers.
In summary, host-based virtualization is a powerful technology that provides a flexible and scalable architecture for deploying and managing virtual machines. It offers numerous advantages, including improved resource utilization, simplified backup and disaster recovery processes, and enhanced data protection. Combined with cloud computing and microservices-based architectures, host-based virtualization enables organizations to embrace a more efficient and agile approach to IT management.
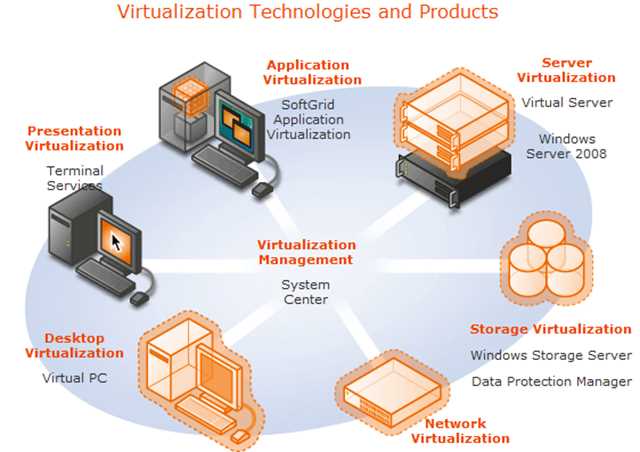
Host-based virtualization, also known as server virtualization, offers numerous benefits to organizations in terms of cloud computing, load balancing, i/o virtualization, and virtualization standards. By utilizing virtualization technology, organizations can optimize their hardware resources and create a scalable architecture that allows for efficient resource utilization.
One of the main benefits of host-based virtualization is the ability to consolidate multiple virtual machines on a single physical machine, resulting in cost savings and increased efficiency. This consolidation allows organizations to achieve higher resource utilization rates, reducing the need for additional hardware and infrastructure.
Moreover, host-based virtualization provides high availability and redundancy through its virtualization models and virtualization capabilities. By creating virtual machines, organizations can ensure that even in the event of hardware failure, their services and applications remain operational.
In addition to its resource efficiency and high availability, host-based virtualization also offers improved security and flexibility. With virtualization solutions, organizations can isolate various operating systems, databases, and storage, minimizing the risk of security breaches or data loss. Furthermore, virtualization allows for easy scalability, enabling organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs without significant infrastructure changes.
Overall, host-based virtualization provides organizations with a flexible and efficient solution for optimizing their resource utilization, improving their infrastructure’s performance, and enhancing their overall IT operations. By leveraging virtualization technology, organizations can maximize their hardware resources, reduce costs, and ensure high availability and scalability for their services and applications.
Host-based virtualization, also known as server virtualization, is a technology that enables the virtualization of one or more servers on a single physical machine. This virtualization capability allows for the efficient allocation and utilization of resources, resulting in cost savings and improved scalability for businesses.
The process of host-based virtualization involves the installation of virtualization software, such as VMware or Hyper-V, on the physical server. This software creates a layer of abstraction between the hardware and the virtual machines, allowing multiple virtual workloads to run independently and securely.
One of the key advantages of host-based virtualization is its ability to partition resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, among the virtual machines. This enables businesses to consolidate their server infrastructure and achieve higher levels of utilization.
Additionally, host-based virtualization provides features like disaster recovery and snapshots, which allow for easy backup and restoration of virtual machines in case of system failures or data loss. This helps businesses ensure high availability and minimize downtime.
Host-based virtualization also addresses performance monitoring and scalability challenges by offering techniques like SR-IOV (Single Root I/O Virtualization) that improve network performance for virtual machines.
Another aspect to consider in host-based virtualization is the impact on system overhead. Virtualization platforms have improved over time, reducing the overhead associated with running virtual machines on a physical server. However, it is essential to consider the potential impact on performance and resource utilization.
Furthermore, host-based virtualization allows for integration with other virtualization standards and technologies, such as rootless containers or virtualization-aware security solutions. This enables businesses to leverage the benefits of different virtualization techniques and enhance their overall infrastructure.
In summary, host-based virtualization offers numerous advantages, including resource consolidation, disaster recovery capabilities, improved scalability, and integration possibilities. By understanding how host-based virtualization works, businesses can make informed decisions about adopting virtualization technologies and optimizing their IT infrastructure.
Host-based virtualization, also known as server virtualization, is a virtualization approach where multiple virtualization systems, or virtual machines, are hosted on a single physical server. This type of virtualization allows for the consolidation of multiple applications and operating systems on a single hardware platform, reducing costs and improving resource utilization.
One of the main types of host-based virtualization is bare metal virtualization. In this approach, the virtualization software runs directly on the server hardware, without the need for an underlying operating system. This allows for improved performance and lower overhead, as there is no additional layer between the virtualization software and the hardware.
Another type of host-based virtualization is containerization, which is a lightweight form of virtualization. In containerization, multiple isolated containers, or virtual environments, share the same operating system kernel. This allows for efficient resource utilization and quick deployment of applications.
Host-based virtualization offers several benefits to organizations. It allows for easy scalability, as new virtual machines can be created and deployed quickly. It also provides improved performance monitoring and management, as administrators can easily monitor the performance of each virtual machine and allocate resources accordingly.
Virtualization also provides enhanced fault tolerance and disaster recovery capabilities. In a virtual infrastructure, virtual machines can be easily backed up and restored in the event of a failure, ensuring business continuity. Live migration performance allows for seamless movement of virtual machines between physical servers, enabling load balancing and reducing downtime.
Furthermore, host-based virtualization enhances security, as each virtual machine is isolated from others, reducing the risk of security breaches. It also supports the implementation of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, as virtual machines can be accessed from any device with an internet connection. Additionally, host-based virtualization enables organizations to take advantage of cloud computing, as virtual machines can be easily deployed and managed in cloud environments.
In summary, host-based virtualization offers various types of deployment methods, including bare metal virtualization and containerization. It provides benefits such as improved virtualization performance, efficient resource utilization, enhanced fault tolerance and disaster recovery, and enhanced security. It is a versatile and powerful technology that is widely used in data centers and cloud computing environments.
Host-based virtualization is a popular virtualization approach that offers several advantages over other virtualization technologies.
One of the key advantages of host-based virtualization is its flexibility in terms of infrastructure provisioning. With host-based virtualization, virtual machines can be easily created and deployed, allowing for efficient use of resources. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where quick deployment and scalability are required, such as in cloud or mobile environments.
Host-based virtualization also provides enhanced monitoring and management capabilities. Virtualization software often includes built-in monitoring tools that allow administrators to easily track the performance and health of virtual machines and the underlying host infrastructure. This enables proactive troubleshooting and ensures optimal performance of virtualized applications.
Another advantage of host-based virtualization is its ability to run multiple operating systems concurrently on a single physical server. This enables organizations to consolidate their infrastructure and reduce hardware costs. Additionally, by encapsulating applications and their dependencies in virtual machines, host-based virtualization offers better isolation and security compared to other virtualization approaches.
High availability is another key benefit offered by host-based virtualization. By leveraging features such as live migration and fault tolerance, host-based virtualization ensures that virtual machines remain highly available even in the event of hardware failures. This improves the overall reliability and uptime of virtualized applications.
Host-based virtualization also provides advanced storage capabilities. Features such as snapshots allow for easy backup and recovery of virtual machines, while technologies like SR-IOV enable direct access to hardware resources, improving virtualization performance.
Furthermore, host-based virtualization can be seamlessly integrated with container orchestration platforms, allowing for the creation and management of both virtual machines and containers within the same infrastructure. This provides organizations with the flexibility to choose the most suitable virtualization technology for their applications and workloads.
In conclusion, host-based virtualization offers numerous advantages over other virtualization technologies. Its flexibility in infrastructure provisioning, enhanced monitoring and management capabilities, support for multiple operating systems, improved security, high availability, advanced storage capabilities, and integration with container orchestration platforms make it an ideal choice for organizations looking to optimize their virtualization performance and reap the benefits of virtualization technology.
Host-based virtualization, also known as server virtualization, is a virtualization technology that allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server. It provides a secure environment for running applications and workloads in virtualization environments.
The key component of host-based virtualization is the hypervisor, which is responsible for creating and managing virtual machines on the physical server. It provides virtualization functions such as resource allocation, load balancing, and high availability to ensure the efficient operation of virtualized workloads.
Another important component of host-based virtualization is SR-IOV (Single Root I/O Virtualization), which allows virtual machines to directly access physical network resources. This enables better performance and flexibility for virtualization deployments that require direct access to network resources.
Data center virtualization is a common use case for host-based virtualization, as it allows organizations to consolidate their physical servers and optimize resource utilization. It also enables the deployment of virtualization technologies for mobile and remote workers, providing them with a secure and flexible environment to access their applications and data.
Virtualization integration is another key component of host-based virtualization, as it allows seamless integration of virtualized workloads with existing infrastructure and management tools. This ensures compatibility and ease of management in heterogeneous IT environments.
While host-based virtualization offers many advantages, such as centralized management, scalability, and flexibility, it also has some disadvantages. These include the potential for performance degradation due to resource contention, and the need for additional hardware resources to support virtualization workloads.
In summary, host-based virtualization is a powerful technology that provides organizations with the ability to efficiently and securely run multiple virtual machines on a single physical server. It offers a range of benefits, including improved resource utilization, high availability, and flexibility for virtualized workloads in diverse environments.
Host-based virtualization, also known as platform virtualization, is a method of virtualization that allows multiple operating systems to run on a single host machine simultaneously. This versatile technology offers a wide range of use cases and is commonly used in various industries.
Host-based virtualization is the foundation of cloud computing, allowing businesses to create and manage virtual machines (VMs) in a cloud environment. With virtualization, businesses can efficiently allocate resources and scale their infrastructure as needed, improving overall efficiency and reducing virtualization costs.
One of the key benefits of host-based virtualization is server consolidation, where multiple physical servers are consolidated into a single host machine. This helps save physical space, reduce power consumption, and streamline management processes, resulting in improved resource utilization and cost savings.
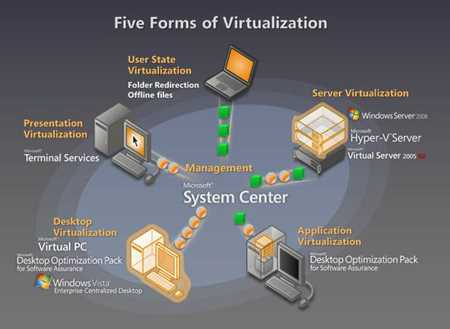
Host-based virtualization enables the use of virtualization management tools that provide centralized management and monitoring of virtualized environments. These tools streamline the deployment, monitoring, and performance analysis of virtual workloads, improving the overall efficiency of virtualization deployments.
Host-based virtualization allows businesses to support Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies by providing virtual workspaces that can be accessed from any device. This enhances flexibility and productivity while ensuring data security and simplifying software updates and patches.
Host-based virtualization enables I/O virtualization, which allows for the efficient sharing and management of I/O devices among multiple VMs. It also supports Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV), a hardware-based technology that improves network performance and reduces latency in virtualized environments.
Host-based virtualization is widely used for web server virtualization, allowing multiple virtual web servers to run on a single physical server. This enables efficient resource allocation and scaling based on varying web traffic, ensuring optimal performance and availability.
Host-based virtualization provides a cost-effective and flexible solution for software development and testing. Developers can create and manage multiple VMs with different operating systems and configurations, allowing for easy testing of software compatibility and reducing the need for physical hardware.
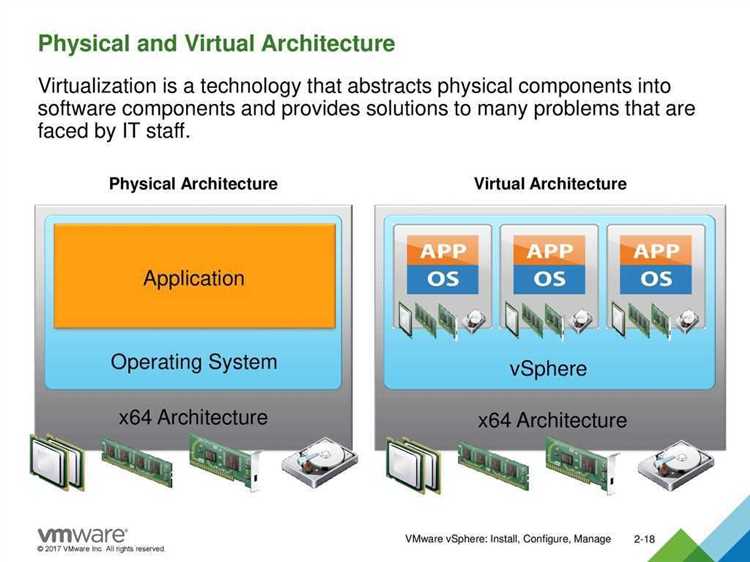
Host-based virtualization can be integrated with Platform as a Service (PaaS) offerings, enabling developers to deploy and manage applications in a virtualized environment. This combination provides developers with a scalable and efficient platform for application development and deployment.
Overall, host-based virtualization offers a wide range of use cases and benefits, including improved resource utilization, cost savings, increased flexibility, and simplified management. Its versatility makes it a valuable technology in various industries, from cloud computing to software development and beyond.
Host-based virtualization, also known as server virtualization, offers a range of benefits such as cost savings, consolidation of resources, and improved load balancing. However, it also brings its fair share of challenges and risks that organizations must consider when implementing this technology.
Performance Monitoring: One of the challenges of host-based virtualization is effectively monitoring the performance of virtual machines (VMs) and their underlying host servers. Organizations must deploy appropriate software tools to ensure optimal performance and identify any bottlenecks or performance issues.
Live Migration: While live migration offers the flexibility to move VMs between hosts without interrupting service, it also presents risks. Organizations need to carefully plan and execute live migration to minimize the impact on performance and avoid potential data loss or downtime.
Fault Tolerance and Disaster Recovery Planning: Host-based virtualization introduces a level of complexity in fault tolerance and disaster recovery planning. Organizations must ensure proper backup and recovery procedures are in place to protect against potential VM failures and ensure business continuity.
Integration and Performance Tuning: Integrating host-based virtualization with existing systems and applications can be a challenging task. It requires careful tuning of performance settings and consideration of compatibility issues to ensure optimal performance and stability.
Virtualization Security: Host-based virtualization introduces new security concerns, such as potential vulnerabilities in hypervisors or the VM isolation. Organizations must implement appropriate security measures and regularly update and patch their virtualization infrastructure.
I/O Virtualization: With multiple VMs running on a host server, I/O virtualization becomes crucial for efficient resource allocation and management. It requires careful configuration and monitoring to ensure optimal I/O performance and avoid potential bottlenecks.
Containerization: Another challenge of host-based virtualization is the management of containerized applications. Organizations must implement container orchestration tools to manage and scale containerized environments effectively.
In conclusion, while host-based virtualization offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges and risks. Organizations need to carefully consider factors such as performance monitoring, live migration, integration, security, and fault tolerance when implementing this technology. Proper planning, monitoring, and evaluation of virtualization functions are essential to maximize the benefits and mitigate potential risks.
Host-based virtualization, also known as hardware virtualization, allows for the creation of multiple virtual machines on a single physical server. This technology has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its numerous advantages.
One of the first steps in implementing host-based virtualization is to choose a virtualization vendor that offers the right virtualization technologies for your needs. It is important to consider factors such as scalability, performance, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
Once you have selected a vendor, it is crucial to perform a thorough virtualization analysis to understand the current state of your infrastructure and identify areas that can benefit from virtualization. This analysis should consider factors such as available resources, workload requirements, and disaster recovery planning.
Virtualization capabilities such as live migration, i/o virtualization, and back-up are essential features to consider when implementing host-based virtualization. These features allow for seamless migration of virtual machines, efficient use of resources, and data protection.
When designing the virtualization environment, it is important to create a scalable architecture that can handle the increasing demands of your workload. This includes considerations such as storage capacity, network bandwidth, and compute power.
There are different virtualization methods to consider, such as paravirtualization and os containers. Each method has its own advantages and it is important to choose the one that best fits your requirements. For example, paravirtualization offers better performance but requires modifications to the guest operating system.
Another important aspect to consider is the management of the virtualization environment. This includes tasks such as monitoring virtualization performance, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring proper security measures are in place.
Finally, when implementing host-based virtualization, it is important to consider the end-user experience. This includes providing a flexible and intuitive user interface, ensuring compatibility with different client devices, and optimizing desktop virtualization for a thick client or thin client environment.
Host-based virtualization technologies continue to evolve and improve, addressing some of the limitations and disadvantages of traditional virtualization solutions. The future of host-based virtualization is focused on performance optimization, security enhancements, and compatibility with diverse hardware and software environments.
Performance optimization is a key area of development in host-based virtualization. As virtualized environments become more common and resource-intensive applications continue to emerge, there is a growing need to improve the performance and efficiency of virtualization technologies. Performance benchmarking and analysis tools are being developed to monitor and optimize the performance of virtual servers and networks.
Memory ballooning is a technique that allows host-based virtualization platforms to dynamically adjust the allocation of memory resources to virtual machines. This helps to optimize memory usage and prevent resource contention, leading to better overall performance in virtualized environments.
Virtualization-aware security is another area of development in host-based virtualization. As the number of virtualized environments increases, the need for effective security measures also grows. Virtualization-aware security solutions are being developed to provide enhanced protection against security threats that specifically target virtualized environments.
Compatibility with various hardware and software configurations is a crucial aspect of host-based virtualization. Virtualization technologies are being designed to be compatible with a wide range of hardware platforms, allowing businesses to adopt virtualization solutions without the need for extensive hardware upgrades.
Network virtualization is another area of development in host-based virtualization. By abstracting network resources and creating virtual networks, businesses can achieve greater flexibility and scalability in their network infrastructure. Network virtualization technologies are being developed to optimize network performance and facilitate the adoption of new technologies like BYOD (Bring Your Own Device).
Storage virtualization is also a significant trend in host-based virtualization. By abstracting storage resources and creating virtual storage pools, businesses can optimize their storage infrastructure and simplify data management. Storage virtualization technologies are being developed to improve data access speeds, reduce storage costs, and enhance data protection.
Rootless containers are a new development in host-based virtualization. Unlike traditional virtual machines that require a hypervisor, rootless containers allow applications to run directly on the host operating system, providing a lightweight and secure virtualization solution.
In conclusion, the future of host-based virtualization is focused on improving performance, enhancing security, ensuring compatibility, and extending virtualization capabilities to network and storage resources. These developments will enable businesses to leverage virtualization technologies for greater efficiency, scalability, and flexibility in their IT infrastructure.
Host-based virtualization, also known as Type 2 virtualization, is a virtualization technology that allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical host machine.
Some benefits of host-based virtualization include improved hardware utilization, increased flexibility and scalability, simplified management and administration, and the ability to isolate and secure virtual environments.
Some future trends in host-based virtualization include the adoption of containerization technologies, such as Docker, the integration of orchestration and management tools for efficient deployment and scaling of virtual environments, and the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence to optimize resource allocation and performance.
Some developments in host-based virtualization include the introduction of hardware-assisted virtualization technologies, such as Intel VT and AMD-V, which provide additional performance and security improvements, the development of hypervisors with minimal overhead and high performance, and the integration of virtualization technologies into cloud computing platforms.
Some challenges in host-based virtualization include security concerns, such as the risk of virtual machine escape attacks, performance overhead due to virtualization layers, and the need for efficient resource management and optimization to ensure maximum utilization of hardware resources.