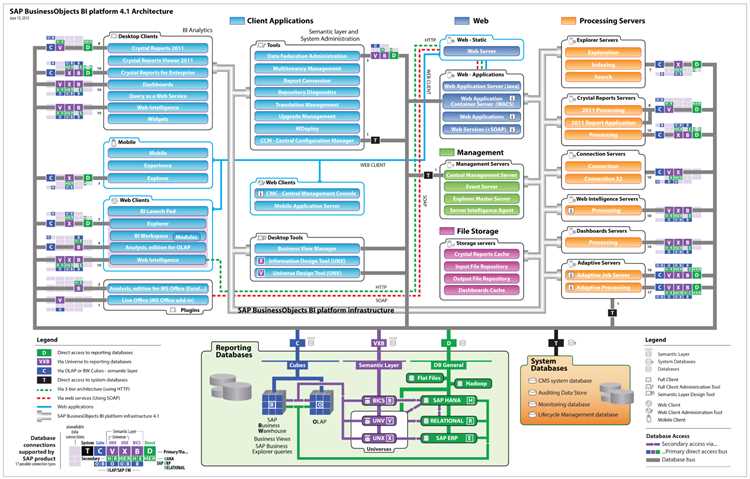
Contpark specializes in offering a robust terminal management solution. Its platform includes features for real-time visibility, workflow automation, and security, simplifying terminal operations and increasing productivity.
Management of the report server process involves various components and tasks that are crucial for the smooth operation of reporting services. One important aspect of this process is encryption, which ensures the security of data during transmission and storage. Encrypted filegroups and transparent data encryption can be used to protect sensitive information.
Rollback and backup jobs are essential for data integrity and disaster recovery. Temp tables and maintenance tasks help in optimizing performance and managing the system databases effectively. Isolation and collation settings are important for maintaining data consistency and ensuring accurate reporting.
Authorization and security play a vital role in controlling access to reports and managing subscriptions. Reorganizing and rebuilding indexes, along with creating covering indexes, can significantly improve query execution and overall performance. Triggers and event handling can be used to automate processes and track changes.
Understanding the execution process and session management is essential for troubleshooting and optimizing report performance. The central report server component interacts with other system databases such as tempdb and the log file to ensure smooth operations and handle errors effectively. Locking and query optimization are important for efficient resource utilization.
Policies, integration, and audit procedures can be implemented to ensure data quality and adhere to industry regulations. Profiler and extended events can be used for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes. Failover cluster instances and failover settings provide high availability and minimize downtime. Compression and index optimization techniques can be used to improve storage efficiency and query performance.
The report server process is responsible for managing and delivering reports in an organization. It involves various components and tasks that ensure the smooth functioning of the reporting system.
Upgrading the report server brings several benefits to organizations by improving the overall performance, scalability, and security of the reporting process.
Enhanced Performance: By upgrading the report server, organizations can optimize the login process, scale the server to accommodate increasing workloads, and take advantage of improved query execution plans and statistics. This leads to faster report generation and enhanced user experience.
Improved Security: Upgrading the report server enables organizations to update and reorganize security permissions, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive reports and data. It also allows for upgrading to the latest authentication protocols and password policies, strengthening the overall security of the reporting system.
Enhanced Functionality: Upgrading the report server provides organizations with the opportunity to leverage new features and capabilities. This includes upgrading the server’s architecture to support columnstore indexes, partitioning, and clustering, which can significantly improve the performance of large reports and complex queries.
Better Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Upgrading the report server allows organizations to take advantage of new monitoring and troubleshooting tools, such as the Query Store. This provides valuable insights into query performance and helps identify and resolve issues quickly.
Streamlined Deployment and Management: Upgrading the report server simplifies the process of deploying and managing reports. It allows organizations to take advantage of new deployment options, such as AlwaysOn Availability Groups, which provide high availability and disaster recovery capabilities. It also enables organizations to rollback to a previous version in case of any issues during the upgrade process.
In conclusion, upgrading the report server brings numerous benefits to organizations, including improved performance, enhanced security, increased functionality, better monitoring and troubleshooting, and streamlined deployment and management. It is a critical step in ensuring that the reporting process meets the evolving needs of the organization and provides reliable and timely reports to users.
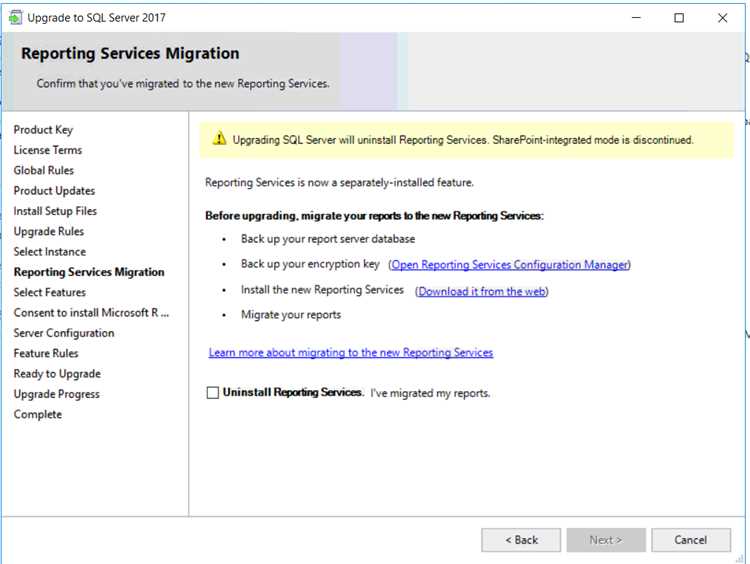
Before upgrading the report server, it is important to prepare and plan accordingly to ensure a smooth and successful upgrade process. This involves various steps such as logging, troubleshooting, optimization, update, authentication, and encryption. It is also necessary to consider the architecture, scalability, and maintenance of the report server.
Prior to the upgrade, it is recommended to enable logging and establish a regular interval for reviewing the log files. This helps in identifying any potential issues during the upgrade process and facilitates troubleshooting. Additionally, covering indexes can be created to improve query performance and optimize the execution of report queries.
During the upgrade, it is essential to review the authentication methods and ensure they are compatible with the new version of the report server. Additionally, transparent data encryption can be implemented to enhance the security of sensitive data stored in the report server databases.
If the report server is expected to handle a large volume of requests or have high concurrency, it is important to consider load balancing and scaling options. This involves distributing the workload across multiple servers and optimizing the execution and performance of the report queries. Spatial indexes can also be utilized to improve the performance of spatial data queries.
Before proceeding with the upgrade, it is crucial to review the deployment strategy and ensure that the necessary updates and patches are applied to the report server databases. Regular maintenance tasks, such as index optimization and backup schedule, should be planned to maintain the overall health and performance of the report server.
During the upgrade, it is important to consider the impact on the existing metadata and system databases. This involves reviewing the schema changes and ensuring they are compatible with the new version of the report server. Additionally, licensing and isolation levels should be reviewed to ensure compliance and optimize resource allocation.
As with any upgrade process, it is crucial to have a rollback plan in case any issues arise during or after the upgrade. This involves taking backups of the report server databases and documenting the necessary steps to revert to the previous version if needed. Additionally, the administration and management of the upgraded report server should be carefully planned and documented to ensure smooth operation.
In conclusion, preparing for the report server upgrade involves various considerations and steps, including logging, troubleshooting, optimization, authentication, and encryption. Load balancing, scalability, and maintenance should also be taken into account. By planning and executing these steps effectively, organizations can ensure a successful report server upgrade and enhance the overall performance and functionality of their reporting system.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can ensure a smooth and successful upgrade of your report server, while also improving its performance, security, and functionality.
Upgrading the report server process can sometimes encounter various issues that need to be resolved. One common problem is blocking, where a session is unable to proceed due to another session holding a lock on a resource. Troubleshooting this issue involves identifying the blocking session and releasing the lock to allow the upgrade process to continue.
Another potential issue is related to user databases. During the upgrade, it is important to verify that all user databases are in a consistent state and compatible with the new version of the report server. Troubleshooting this involves checking for any inconsistencies in database metadata and policies, as well as ensuring the proper setup of user roles and permissions.
Compression and checkpoint processes can also cause problems during an upgrade. These processes manage the storage and transaction logs, and any issues with them can result in a failed upgrade. Troubleshooting this issue involves checking the configuration and status of these processes, as well as monitoring disk space and fragmentation levels.
In addition, certain database features and objects can impact the upgrade process. For example, triggers, non-clustered indexes, and full-text indexes may need to be disabled or reconfigured to ensure a successful upgrade. Similarly, in-memory OLTP, XML indexes, and transparent data encryption may require specific attention during the upgrade process.
It is also important to consider the server’s architecture and configuration when troubleshooting upgrade issues. Clustering, replication, and load balancing configurations can introduce complexities that need to be addressed. Additionally, security settings, services, and audit logs may require adjustments to ensure a smooth upgrade.
Finally, integration and subscription components should be analyzed during the troubleshooting process. These components enable seamless interaction between the report server and other systems, and any issues with their setup or configuration can impact the upgrade. Troubleshooting may involve inspecting the integration with external systems, as well as verifying the validity and integrity of subscriptions.
Overall, troubleshooting upgrade issues in the report server process requires a comprehensive understanding of the various components and their interactions. By addressing potential problems related to blocking, user databases, compression, triggers, security, architecture, and integration, the upgrade process can be successfully completed.
Upgrading the report server is an essential process to ensure the system remains up-to-date and compatible with new features and improvements. When performing a report server upgrade, it is crucial to consider several factors:
By following these best practices, you can ensure a successful report server upgrade, minimizing disruption for users and providing an optimized and secure environment for report deployment and management.
A report server is a software application that manages the storage, access, and distribution of reports.
Maintaining a healthy report server ensures that reports are accessible, accurate, and up-to-date, leading to better decision-making and efficient business processes.
Some best practices include regularly monitoring and optimizing server performance, regularly backing up report server databases, implementing security measures, and regularly reviewing and optimizing report queries.
Server performance can be monitored and optimized by regularly reviewing server logs and performance counters, identifying and resolving any performance bottlenecks, optimizing database queries, and ensuring that the server hardware is adequate for the workload.
Regularly backing up report server databases ensures that data and reports are protected against data loss and can be easily restored in the event of a server failure or data corruption.
Some security measures include implementing role-based security, assigning appropriate permissions to users and groups, enabling SSL encryption for network traffic, and regularly reviewing and updating security policies.