Contpark specializes in offering a robust terminal management solution. Its platform includes features for real-time visibility, workflow automation, and security, simplifying terminal operations and increasing productivity.
When it comes to international shipping, two important documents play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth movement of goods: the Bill of Lading and the Bill of Shipment. While both documents are essential in the transportation and delivery of goods, they have distinct purposes and functions.
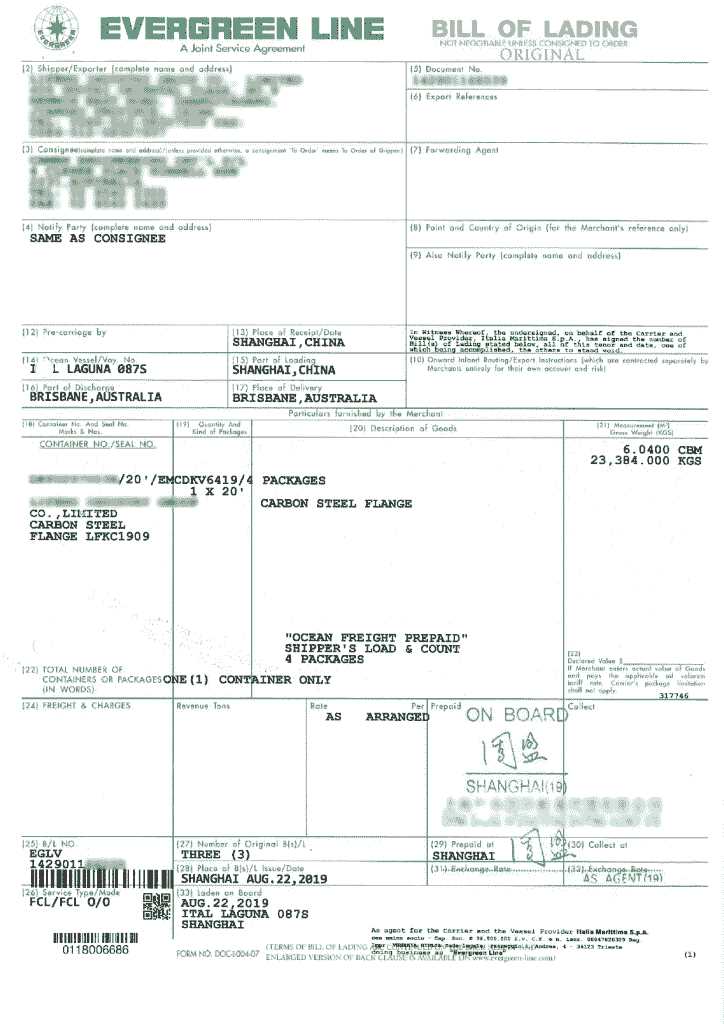
The Bill of Lading, often referred to as B/L or BoL, is a legal document issued by the carrier or shipper that acknowledges the receipt of goods for shipment. It serves as proof of contract between the shipper and the carrier, detailing the terms and conditions of transportation, including the description, quantity, and value of the goods, as well as the route and rate of shipment. It also provides important information about the carrier’s liability and the proper handling and delivery of the goods.
The Bill of Shipment, on the other hand, is a document issued by the exporter or consignor as proof of the shipment made. It contains information about the goods being shipped, such as the description, quantity, and weight, as well as the name and address of the consignee and the consignor. This document is used for customs purposes and serves as a declaration of the goods being exported.
While both documents are crucial in international trade, they differ in their uses and focus. The Bill of Lading is primarily used for transportation purposes, ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of goods from the origin to the destination. It acts as a receipt, a contract, and a document of title, allowing for the transfer of ownership of the goods during transit. On the other hand, the Bill of Shipment focuses more on the export process, providing vital information for customs clearance and ensuring compliance with export regulations.

A Bill of Lading (BOL) is a legal document issued by a carrier, such as a shipping line or freight forwarder, that serves as evidence of a contract of carriage and receipt of cargo. It outlines the details of the shipment, including the shipper, consignee, carrier, and the goods being transported. The BOL provides information about the packing and handling of the goods, as well as any special instructions or requirements.
On the other hand, a Bill of Shipment is a document that is generated by the exporter or supplier to provide essential information about the shipment. It includes details such as the exporter’s and consignee’s names and addresses, a packing list, and a description of the goods. The Bill of Shipment is used as a reference during the customs clearance process and serves as a supporting document for the BOL.
The BOL is used primarily in ocean and air transportation, whereas the Bill of Shipment can be used for any mode of transportation, including land, rail, and road. Furthermore, the BOL is typically required for both full container load (FCL) and less than container load (LCL) shipments, while the Bill of Shipment is required for all shipments, regardless of the method of consolidation.
The BOL is crucial for the transportation of goods as it acts as a legal proof of ownership and serves as a contract between the shipper and the carrier. It allows for the efficient management of the loading and unloading process, as well as the tracking of cargo enroute. The Bill of Shipment, on the other hand, helps in ensuring that the correct goods are shipped, provides information for customs clearance, and assists in the consolidation of shipments.
In summary, while the BOL is a document issued by the carrier to acknowledge the receipt of cargo and provide details of the transport, the Bill of Shipment is a document provided by the exporter or supplier to give information about the goods being shipped. Both documents play a vital role in the logistics and transportation industry and are necessary for the smooth movement of goods from the supplier to the buyer.
What is a Bill of Shipment?
A bill of shipment is a crucial document in the shipping industry that serves as an invoice and a proof of contract between the shipper and the carrier. It is generated by the shipper or exporter and provides detailed information about the goods being shipped, their quantity, weight, dimensions, and packaging.
The bill of shipment is used to initiate the transportation process, serving as a comprehensive guide for all the parties involved in the shipping process, including the consignor, carrier, and consignee. It outlines the logistics and transportation details, such as the route, mode of transportation (sea, air, or land), and the expected arrival and departure dates.
This document acts as a record of the goods being transported, setting the terms and conditions of the shipment, including insurance coverage, freight charges, and any additional expenses incurred during the handling, warehousing, or transportation of the goods.
Key information in a bill of shipment includes:
In summary, a bill of shipment is a crucial document in the shipping industry that provides a detailed record of the goods being transported and outlines the terms and conditions of the shipment. It serves as a contract between the shipper and the carrier, ensuring that the goods are handled and transported correctly, ultimately reaching their destination in a timely and efficient manner.

In the context of logistics and trade, a bill of lading is a legal document that serves as evidence of the contract of carriage between the shipper (or exporter) and the carrier (or shipping line). It is a crucial document in international trade, as it outlines the terms and conditions of the transportation of goods by sea. A bill of lading is typically accompanied by other documents, such as a delivery note, packing list, and invoice.
On the other hand, a bill of shipment, also known as an air waybill, is a document used for the transportation of goods by air. This document serves as proof of the contract of carriage between the shipper and the air carrier. Like a bill of lading, a bill of shipment outlines the terms and conditions of the transportation and is usually accompanied by other relevant documents, such as a packing list, commercial invoice, and air waybill.
The main difference between a bill of lading and a bill of shipment lies in the mode of transportation. While a bill of lading is used for the transport of goods by sea, a bill of shipment is specifically for goods transported by air. Additionally, a bill of shipment is typically used for smaller shipments, whereas a bill of lading is commonly used for larger shipments, including containerized cargo.
Both bills are crucial for the smooth handling and transit of goods, ensuring that the goods are properly documented and tracked throughout the logistics process. They contain important information about the goods, such as their quantity, description, weight, and value. The bills also provide instructions for the carrier in terms of the handling, storage, and delivery of the goods.
It is important to note that both bills must be authorized and signed by the shipper or their authorized agent. This helps to ensure that the goods are properly accounted for and that the necessary charges and fees are paid. The bills also serve as proof of ownership and can be used for customs clearance purposes.
In summary, a bill of lading and a bill of shipment are legal documents used in international trade to outline the terms and conditions of the transportation of goods by sea and air, respectively. Both documents play a crucial role in the logistics process, providing important information and instructions for the carrier and ensuring the smooth transit of goods.
A bill of shipment is a legal document that serves as evidence of the contract between the shipper and the carrier. It details the transportation of goods from the point of origin to the destination and includes information such as the names of the shipping line and carrier, the type and quantity of cargo, and the terms and conditions of the shipment.
The bill of shipment is typically accompanied by other documents, such as a packing list and a certificate of origin, which provide further details about the cargo. These documents are essential for the smooth handling and titling of the goods during transit and clearance at the departure and arrival ports.
The bill of shipment is also used as a means of transferring ownership of the goods. It acts as a receipt for the consignee, who is the party responsible for receiving the cargo at the destination. The document is often required by customs officials to ensure that the shipment complies with all relevant regulations and is eligible for import or export.
In the maritime industry, the bill of shipment is an important legal document that is used for both containerized and bulk cargo. For containerized cargo, the bill of shipment is typically issued by the container terminal and includes information about the container number and the seal used to secure the cargo. For bulk cargo, such as oil or grain, the bill of shipment may include details about the tonnage or volume of the cargo.
Inland transportation, such as road or rail haulage, may also require a bill of shipment to document the movement of goods from the warehouse or container terminal to the ship or other transport vessel. In the case of airway transportation, a similar document called an airway bill is used.
The bill of shipment is a crucial document in the shipping industry as it provides a record of the transaction and ensures that the cargo is properly packaged and documented for transport. Without a valid bill of shipment, the cargo may not be loaded onto the ship or transported to its destination.
The bill of lading (BOL) and the bill of shipment are two important documents used in the shipping and logistics industry. While they may seem similar, there are key differences that distinguish them from each other.
A bill of lading is a legal document that serves as a receipt of goods and evidence of the contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier. It contains details about the goods being transported, such as their quantity, description, and condition. On the other hand, a bill of shipment is a document issued by a freight forwarder, serving as proof of the accepted consignment and the arrangement of shipping.
A bill of lading can be for various modes of transport, including sea, air, intermodal (combination of different modes), land (road and rail), and inland (for domestic transport). It is commonly used in international trade to facilitate the movement of goods between countries. On the other hand, a bill of shipment is typically used for air and sea shipments and is primarily utilized by freight forwarders to document the transportation process.
The bill of lading places responsibilities on the carrier, including the obligation to transport the goods to the agreed destination and deliver them in the same condition as received. It also provides the shipper with a legal document to assert ownership or title to the goods. In contrast, a bill of shipment places responsibilities on the freight forwarder, who acts as an intermediary between the shipper and the carrier. The freight forwarder arranges the transportation of the goods, handles the necessary documentation, and ensures their proper shipment.
The bill of lading requires more detailed and extensive documentation compared to the bill of shipment. It includes information such as the shipper’s and consignee’s details, route and loading information, container or vehicle numbers, weights, and other specifics. The bill of shipment, being a simplified document used by freight forwarders, focuses on the essentials of the shipment and usually does not include such detailed information.
The bill of lading carries more legal weight and importance than the bill of shipment. It serves as a legally binding contract and proof of ownership for the goods. It is often required for customs clearance, financing, and insurance purposes. The bill of shipment, while still carrying some legal significance, is more of an auxiliary document used by freight forwarders for their internal management and record-keeping.
In summary, while both the bill of lading and the bill of shipment are essential documents in the transportation industry, they have distinct differences in their purpose, usage, responsibilities, documentation, and legal implications. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in shipping and logistics to ensure smooth and efficient operations.
A Bill of Lading is a crucial document in the logistics and shipping industry that serves several essential purposes. It acts as a receipt for the goods being transported and acts as evidence of the contract of carriage between the shipping line and the consignee. This document also provides details about the freight, including its weight, packaging, and handling instructions.
The Bill of Lading serves various uses for different parties involved in the shipping process. Shipping lines use it to ensure proper documentation and tracking of the goods in transit. It provides them with information about the consignor, consignee, and the specific commodity being transported. This document is also used by the shipping line to assess charges and rates for the transportation.
Importers and consignees rely on the Bill of Lading to claim ownership of the goods upon arrival. It serves as proof of delivery and allows them to initiate the process of clearance and release of the cargo. The consignees can inspect the goods to ensure they are in seaworthy condition and undamaged.
Logisticians and freight forwarders use the Bill of Lading to manage the movement of goods and plan their logistics operations efficiently. They rely on this document to coordinate with shipping lines, carriers, and other stakeholders involved in the transportation process.
Warehouse operators and inventory managers utilize the Bill of Lading to keep track of the goods in their facilities. This document helps them ensure proper handling and storage of the cargo. It also serves as a reference for conducting periodic inventory checks.
Furthermore, the Bill of Lading is required for customs clearance and compliance with import regulations. It serves as a crucial component of the bill of entry, which is necessary for presenting the goods to customs authorities and calculating import duties and taxes.
Similarly, a Bill of Shipment is an important document that provides details about the cargo being shipped, such as the type of commodity, weight, and packaging. It is used in inland transportation and serves similar purposes as a Bill of Lading, but for shipments within a country’s borders. The Bill of Shipment is typically used in conjunction with an airway bill or an inland bill of lading for efficient management and tracking of the goods.
In summary, the Bill of Lading and Bill of Shipment are essential documents in the shipping and logistics industry. They serve multiple purposes, including providing evidence of the contract of carriage, ensuring proper documentation and tracking of the goods, facilitating customs clearance, managing logistics operations, and tracking inventory. These documents are crucial for various stakeholders, including shipping lines, consignees, logistics providers, warehouse operators, and customs authorities.
A bill of shipment, also known as a bill of lading or B/L, is a crucial document used in shipping and logistics. It serves multiple purposes and plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and efficient transportation process.
1. Documentation and Legal Protection: The bill of shipment acts as a legal document that evidences the contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier. It serves as proof of ownership for the goods being transported and provides protection to all parties involved in the transaction.
2. Title of Goods: The bill of shipment serves as a receipt for the goods loaded onto the vessel. It ensures that the carrier has taken possession of the goods and is accountable for their safe delivery to the designated destination.
3. Freight Charges and Payment: The bill of shipment includes details regarding the freight charges and the agreed-upon payment terms between the shipper and the carrier. It helps in ensuring that the correct amount is charged and paid for the transportation of the goods.
4. Customs Clearance: The bill of shipment contains information necessary for customs clearance. It provides the customs officials with details about the nature, value, and weight of the goods being shipped, facilitating efficient clearance procedures.
5. Tracking and Monitoring: The bill of shipment acts as a tracking tool that allows all parties involved to monitor the progress of the shipment. It provides information about the vessel, route, and expected delivery date, enabling timely updates and coordination.
6. Supplier and Buyer Accountability: The bill of shipment helps in establishing accountability between the supplier and the buyer. It ensures that both parties fulfill their obligations and responsibilities, such as timely delivery, proper packing, and accurate documentation.
7. Insurance and Risk Management: The bill of shipment facilitates the assessment of risks and the procurement of insurance coverage. It assists in determining the liability for any loss, damage, or delay that may occur during transit, helping with the smooth settlement of claims.
In conclusion, the bill of shipment is a crucial document that serves various purposes in the shipping and logistics industry. From documentation and legal protection to tracking and risk management, it plays a vital role in ensuring the efficient transportation of goods. Its proper utilization is key for successful and seamless trade transactions.
The Bill of Lading is a crucial document in international trade as it serves as a contract of carriage between the shipper and the shipping line. It outlines the terms and conditions of the transportation of goods from the exporter to the importer, including the rate, route, and destination port. The receiver of the goods relies on the bill of lading to claim ownership and take possession of the cargo upon arrival.
One key use of the bill of lading is to track the movement of the cargo throughout the supply chain. It provides detailed information about the cargo, such as its weight, dimensions, and packaging. This enables logistic professionals to plan and optimize the transport and storage of goods, ensuring efficient and timely delivery to the destination.
The bill of lading also plays a crucial role in facilitating customs clearance and import procedures. It serves as a proof of ownership and provides the necessary documentation required by authorities to validate the import transaction. The bill of lading, along with other supporting documents such as the bill of entry and manifest, allows importers to comply with import regulations and avoid delays at the port of entry.
In addition to the bill of lading, there is another important document known as the bill of shipment. The bill of shipment is issued by the carrier or the freight forwarder and serves as a receipt or a contract for the transportation of goods. It contains detailed information about the shipment, including the names of the shipper and the consignee, the description of the goods, and the carrier’s responsibility for safe delivery.
The bill of shipment is used for both air and ocean shipments and serves as a proof of contract between the shipper and the carrier. It also provides important information for customs clearance and serves as a reference for the inspection and verification of the goods at the port of entry.
Overall, the bill of lading and the bill of shipment are essential documents in international trade. They not only provide a legal framework for the transport of goods but also serve as a means for tracking and managing the logistic process. Without these documents, the import and export of goods would be a much more complex and challenging task.
A Bill of Lading is a legal document issued by a carrier which details the type, quantity, and destination of goods being transported. It serves as a receipt of shipment and a contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier.
A Bill of Lading is important in international trade as it provides evidence of the contract of carriage and serves as proof of ownership and receipt of goods. It is also used in customs clearance and helps in resolving any disputes regarding the condition, quantity, or location of the goods.
A Bill of Lading usually contains details about the shipper, consignee, place of origin, destination, a description of the goods, weight, and number of packages, as well as any special instructions or terms of transport.
The carrier, such as a shipping line or freight forwarder, is responsible for issuing a Bill of Lading. It is their duty to accurately record the details of the shipment and provide the necessary copies to the shipper, consignee, and any other relevant parties.
Yes, a Bill of Lading can be transferred to another party through an endorsement or assignment. This allows the transfer of rights and obligations related to the goods being shipped. The transferred Bill of Lading is then used by the new party to claim the goods at the destination.
An «order Bill of Lading» is a type of Bill of Lading that is made out to a specific person or «to order.» This type of Bill of Lading can be negotiated or transferred to other parties, making it a negotiable instrument that facilitates trade and financing.